A multitrait genetic study of hemostatic factors and hemorrhagic transformation after stroke treatment
- PMID: 38103737
- PMCID: PMC11103592
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtha.2023.11.027
A multitrait genetic study of hemostatic factors and hemorrhagic transformation after stroke treatment
Abstract
Background: Thrombolytic recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (r-tPA) treatment is the only pharmacologic intervention available in the ischemic stroke acute phase. This treatment is associated with an increased risk of intracerebral hemorrhages, known as hemorrhagic transformations (HTs), which worsen the patient's prognosis.
Objectives: To investigate the association between genetically determined natural hemostatic factors' levels and increased risk of HT after r-tPA treatment.
Methods: Using data from genome-wide association studies on the risk of HT after r-tPA treatment and data on 7 hemostatic factors (factor [F]VII, FVIII, von Willebrand factor [VWF], FXI, fibrinogen, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, and tissue plasminogen activator), we performed local and global genetic correlation estimation multitrait analyses and colocalization and 2-sample Mendelian randomization analyses between hemostatic factors and HT.
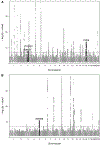
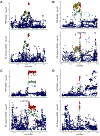
Results: Local correlations identified a genomic region on chromosome 16 with shared covariance: fibrinogen-HT, P = 2.45 × 10-11. Multitrait analysis between fibrinogen-HT revealed 3 loci that simultaneously regulate circulating levels of fibrinogen and risk of HT: rs56026866 (PLXND1), P = 8.80 × 10-10; rs1421067 (CHD9), P = 1.81 × 10-14; and rs34780449, near ROBO1 gene, P = 1.64 × 10-8. Multitrait analysis between VWF-HT showed a novel common association regulating VWF and risk of HT after r-tPA at rs10942300 (ZNF366), P = 1.81 × 10-14. Mendelian randomization analysis did not find significant causal associations, although a nominal association was observed for FXI-HT (inverse-variance weighted estimate [SE], 0.07 [-0.29 to 0.00]; odds ratio, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.75-1.00; raw P = .05).
Conclusion: We identified 4 shared loci between hemostatic factors and HT after r-tPA treatment, suggesting common regulatory mechanisms between fibrinogen and VWF levels and HT. Further research to determine a possible mediating effect of fibrinogen on HT risk is needed.
Keywords: fibrinogen; hemorrhagic transformation; hemostatic factors; r-tPA treatment; von Willebrand factor.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interests There are no competing interests to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Tsao CW, Aday AW, Almarzooq ZI, Alonso A, Beaton AZ, Bittencourt MS, Boehme AK, Buxton AE, Carson AP, Commodore-Mensah Y, Elkind MSV, Evenson KR, Eze-Nliam C, Ferguson JF, Generoso G, Ho JE, Kalani R, Khan SS, Kissela BM, Knutson KL, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2022 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2022;145:e153–639. - PubMed
-
- Del Río-Espínola A, Fernández-Cadenas I, Giralt D, Quiroga A, Gutiérrez-Agullõ M, Quintana M, Fernández-Álvarez P, Domingues-Montanari S, Mendiõroz M, Delgado P, Turck N, Ruíz A, Ribó M, Castellanos M, Obach V, Martínez S, Freijo MM, Jiménez-Conde J, Cuadrado-Godia E, Roquer J,, et al. A predictive clinical-genetic model of tissue plasminogen activator response in acute ischemic stroke. Ann Neurol. 2012;72:716–29. - PubMed
-
- Hacke W, Donnan G, Fieschi C, Kaste M, von Kummer R, Broderick JP, Brott T, Frankel M, Grotta JC, Haley EC Jr, Kwiatkowski T, Levine SR, Lewandowski C, Lu M, Lyden P, Marler JR, Patel S, Tilley BC, Albers G, Bluhmki E, et al. Association of outcome with early stroke treatment: pooled analysis of ATLANTIS, ECASS, and NINDS rt-PA stroke trials. Lancet. 2004;363:768–74. - PubMed
-
- Wahlgren N, Ahmed N, Dávalos A, Hacke W, Millán M, Muir K, Roine RO, Toni D, Lees KR, investigators SITS. Thrombolysis with alteplase 3–4.5 h after acute ischaemic stroke (SITS-ISTR): an observational study. Lancet. 2008;372:1303–9. - PubMed
-
- IST-3 collaborative group, Sandercock P, Wardlaw JM, Lindley RI, Dennis M, Cohen G, Murray G, Innes K, Venables G, Czlonkowska A, Kobayashi A, Ricci S, Murray V, Berge E, Slot KB, Hankey GJ, Correia M, Peeters A, Matz K, Lyrer P, Gubitz Gord, et al. The benefits and harms of intravenous thrombolysis with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator within 6 h of acute ischaemic stroke (the third international stroke trial [IST-3]): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2012;379:2352–63. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

