The rise of epitranscriptomics: recent developments and future directions
- PMID: 38103979
- PMCID: PMC10843569
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tips.2023.11.002
The rise of epitranscriptomics: recent developments and future directions
Abstract
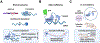
The epitranscriptomics field has undergone tremendous growth since the discovery that the RNA N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification is reversible and is distributed throughout the transcriptome. Efforts to map RNA modifications transcriptome-wide and reshape the epitranscriptome in disease settings have facilitated mechanistic understanding and drug discovery in the field. In this review we discuss recent advancements in RNA modification detection methods and consider how these developments can be applied to gain novel insights into the epitranscriptome. We also highlight drug discovery efforts aimed at developing epitranscriptomic therapeutics for cancer and other diseases. Finally, we consider engineering of the epitranscriptome as an emerging direction to investigate RNA modifications and their causal effects on RNA processing at high specificity.
Keywords: N(6)-methyladenosine; RNA modifications; drug development; epitranscriptomics; machine learning; nanopore sequencing; pseudouridine.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests C.H. is a scientific founder, member of the scientific advisory board, and equity holder of Aferna Bio Inc. and AccuaDX Inc.; a scientific co-founder and equity holder of Accent Therapeutics Inc.; and a member of the scientific advisory board of Rona Therapeutics. No interests are declared by the remaining authors.
Figures


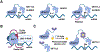
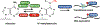
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

