Self-assembly of H2S-responsive nanoprodrugs based on natural rhein and geraniol for targeted therapy against Salmonella Typhimurium
- PMID: 38104180
- PMCID: PMC10725032
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-023-02256-9
Self-assembly of H2S-responsive nanoprodrugs based on natural rhein and geraniol for targeted therapy against Salmonella Typhimurium
Abstract
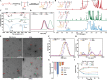
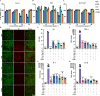
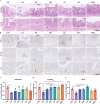
Salmonellosis is a globally extensive food-borne disease, which threatens public health and results in huge economic losses in the world annually. The rising prevalence of antibiotic resistance in Salmonella poses a significant global concern, emphasizing an imperative to identify novel therapeutic agents or methodologies to effectively combat this predicament. In this study, self-assembly hydrogen sulfide (H2S)-responsive nanoprodrugs were fabricated with poly(α-lipoic acid)-polyethylene glycol grafted rhein and geraniol (PPRG), self-assembled into core-shell nanoparticles via electrostatic, hydrophilic and hydrophobic interactions, with hydrophilic exterior and hydrophobic interior. The rhein and geraniol are released from self-assembly nanoprodrugs PPRG in response to Salmonella infection, which is known to produce hydrogen sulfide (H2S). PPRG demonstrated stronger antibacterial activity against Salmonella compared with rhein or geraniol alone in vitro and in vivo. Additionally, PPRG was also able to suppress the inflammation and modulate gut microbiota homeostasis. In conclusion, the as-prepared self-assembly nanoprodrug sheds new light on the design of natural product active ingredients and provides new ideas for exploring targeted therapies for specific Enteropathogens. Graphical illustration for construction of self-assembly nanoprodrugs PPRG and its antibacterial and anti-inflammatory activities on experimental Salmonella infection in mice.
Keywords: Geraniol; H2S-responsive nanoprodrugs; PPRG; Rhein; Salmonella infection; Self-assembly.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Orszagh E, Pitter JG, Kalo Z, Voko Z, Jozwiak A. Retrospective cost-utility analysis of the Non-typhoidal Salmonella control programme in Hungary. Food Control. 2021 doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2020.107529. - DOI
-
- Wang XC, Biswas S, Paudyal N, Pan H, Li XL, Fang WH, Yue M. Antibiotic resistance in Salmonella Typhimurium isolates recovered from the food chain through national antimicrobial resistance monitoring system between 1996 and 2016. Front Microbiol. 2020 doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00985. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 32121004/Foundation for Innovative Research Groups of the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2020B0301030007/Guangdong Major Project of Basic and Applied Basic Research
- 2020B0301030007/Guangdong Major Project of Basic and Applied Basic Research
- 2019BT02N054/Local Innovative and Research Teams Project of Guangdong Pearl River Talents Program
- NT2021006/Laboratory of Lingnan Modern Agriculture Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

