Targeting the RAS/RAF/MAPK pathway for cancer therapy: from mechanism to clinical studies
- PMID: 38105263
- PMCID: PMC10725898
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-023-01705-z
Targeting the RAS/RAF/MAPK pathway for cancer therapy: from mechanism to clinical studies
Abstract
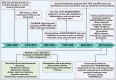
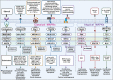
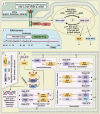
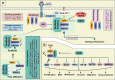
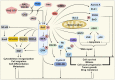
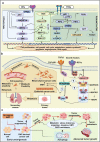
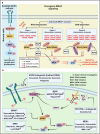
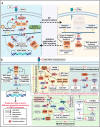
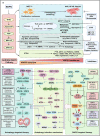
Metastatic dissemination of solid tumors, a leading cause of cancer-related mortality, underscores the urgent need for enhanced insights into the molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying metastasis, chemoresistance, and the mechanistic backgrounds of individuals whose cancers are prone to migration. The most prevalent signaling cascade governed by multi-kinase inhibitors is the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, encompassing the RAS-RAF-MAPK kinase (MEK)-extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK) pathway. RAF kinase is a primary mediator of the MAPK pathway, responsible for the sequential activation of downstream targets, such as MEK and the transcription factor ERK, which control numerous cellular and physiological processes, including organism development, cell cycle control, cell proliferation and differentiation, cell survival, and death. Defects in this signaling cascade are associated with diseases such as cancer. RAF inhibitors (RAFi) combined with MEK blockers represent an FDA-approved therapeutic strategy for numerous RAF-mutant cancers, including melanoma, non-small cell lung carcinoma, and thyroid cancer. However, the development of therapy resistance by cancer cells remains an important barrier. Autophagy, an intracellular lysosome-dependent catabolic recycling process, plays a critical role in the development of RAFi resistance in cancer. Thus, targeting RAF and autophagy could be novel treatment strategies for RAF-mutant cancers. In this review, we delve deeper into the mechanistic insights surrounding RAF kinase signaling in tumorigenesis and RAFi-resistance. Furthermore, we explore and discuss the ongoing development of next-generation RAF inhibitors with enhanced therapeutic profiles. Additionally, this review sheds light on the functional interplay between RAF-targeted therapies and autophagy in cancer.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Unraveling the interplay between RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK signaling pathway and autophagy in cancer: From molecular mechanisms to targeted therapy.Biochem Pharmacol. 2023 Nov;217:115842. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115842. Epub 2023 Oct 5. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37802240 Review.
-
Targeting the Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the treatment of cancer.Oncogene. 2007 May 14;26(22):3291-310. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210422. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 17496923 Review.
-
RAF inhibitors prime wild-type RAF to activate the MAPK pathway and enhance growth.Nature. 2010 Mar 18;464(7287):431-5. doi: 10.1038/nature08833. Epub 2010 Feb 3. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20130576
-
Roles of the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in leukemia therapy.Leukemia. 2011 Jul;25(7):1080-94. doi: 10.1038/leu.2011.66. Epub 2011 Apr 15. Leukemia. 2011. PMID: 21494257 Review.
-
KLF4 is regulated by RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK signaling through E2F1 and promotes melanoma cell growth.Oncogene. 2017 Jun 8;36(23):3322-3333. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.481. Epub 2017 Jan 9. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 28068326 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Multiple myeloma: signaling pathways and targeted therapy.Mol Biomed. 2024 Jul 4;5(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s43556-024-00188-w. Mol Biomed. 2024. PMID: 38961036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting CD44 and other pleiotropic co-receptors as a means for broad inhibition of tumor growth and metastasis.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2024 Oct;41(5):599-611. doi: 10.1007/s10585-024-10292-4. Epub 2024 May 18. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2024. PMID: 38761292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mutational characteristics of extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma analyzed in relation to clinical prognostic indices.Ann Hematol. 2024 Dec;103(12):5749-5757. doi: 10.1007/s00277-024-06035-w. Epub 2024 Nov 26. Ann Hematol. 2024. PMID: 39589496
-
PIS as a regulator of cellular heterogeneity, prognostic significance, and immune landscape in thyroid cancer.Transl Oncol. 2025 May;55:102296. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2025.102296. Epub 2025 Mar 24. Transl Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40132388 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Genetic Orchestra of Cancer: The Interplay Between Oncogenes and Tumor-Suppressor Genes.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Mar 24;17(7):1082. doi: 10.3390/cancers17071082. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40227591 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

