Artificial viruses: A nanotechnology based approach
- PMID: 38105369
- PMCID: PMC11087390
- DOI: 10.1007/s40199-023-00496-6
Artificial viruses: A nanotechnology based approach
Abstract
Objectives: The main objective of this work was to review and summarise the detailed literature available on viral nanoparticle and the strategies utilised for their manufacture along with their applications as therapeutic agents.
Data acquisition: The reported literature related to development and application of virus nanoparticles have been collected from electronic data bases like ScienceDirect, google scholar, PubMed by using key words like "viral nanoparticles", "targeted drug delivery" and "vaccines" and related combinations.
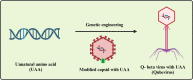
Result: From the detailed literature survey, virus nanoparticles were identified as carriers for the targeted delivery. Due to the presence of nanostructures in virus nanoparticles, these protect the drugs from the degradation in the gastrointestinal tract and in case of the delivery of gene medicine, they carry the nucleic acids to the target/susceptible host cells. Thus, artificial viruses are utilised for targeted delivery to specific organ in biomedical and biotechnological areas.
Conclusion: Thus, virus nanoparticles can be considered as viable option as drug/gene carrier in various healthcare sectors especially drug delivery and vaccine and can be explored further in future for the development of better drug delivery techniques.
Keywords: Drug delivery; Nano technology; Therapy; Virus gene.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Figures








Similar articles
-
A Mini-Review on Nano Technology in the Tumour Targeting Strategies: Drug Delivery to Cancer Cells.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2020;20(17):2012-2024. doi: 10.2174/1871520620666200804103714. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32753024 Review.
-
Nanotechnology for delivery of peptide nucleic acids (PNAs).J Control Release. 2016 Oct 28;240:302-311. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.01.005. Epub 2016 Jan 8. J Control Release. 2016. PMID: 26776051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Virus-Based Nanoparticles as Versatile Nanomachines.Annu Rev Virol. 2015 Nov;2(1):379-401. doi: 10.1146/annurev-virology-100114-055141. Epub 2015 Sep 25. Annu Rev Virol. 2015. PMID: 26958921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent progress in applications of nanoparticles in fish medicine: A review.Nanomedicine. 2016 Apr;12(3):701-710. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2015.11.005. Epub 2015 Dec 2. Nanomedicine. 2016. PMID: 26656532 Review.
-
A framework for designing delivery systems.Nat Nanotechnol. 2020 Oct;15(10):819-829. doi: 10.1038/s41565-020-0759-5. Epub 2020 Sep 7. Nat Nanotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32895522 Review.
Cited by
-
Research advancements in nanoparticles and cell-based drug delivery systems for the targeted killing of cancer cells.Oncol Res. 2024 Dec 20;33(1):27-44. doi: 10.32604/or.2024.056955. eCollection 2025. Oncol Res. 2024. PMID: 39735681 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

