Oncological Applications of Quantum Machine Learning
- PMID: 38105500
- PMCID: PMC10729620
- DOI: 10.1177/15330338231215214
Oncological Applications of Quantum Machine Learning
Abstract
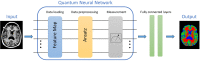
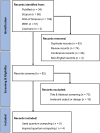
Background: Cancer is a leading cause of death worldwide. Machine learning (ML) and quantum computers (QCs) have recently advanced significantly. Numerous studies have examined the application of quantum machine learning (QML) in healthcare and validated its superiority over classical ML algorithms. Objectives: This review investigates and reports the oncological applications of QML. Methods: In March 2023, an electronic investigation of PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, IEEE, and Cochrane databases was performed. The articles were screened based on titles and abstracts, and their full texts were examined. Results: Initially, a total of 207 articles were retrieved. Thereafter, 9 articles were included in the study, most of which were published from 2020 onwards. The results indicated the implementation of various QML techniques in different aspects of oncology, such as reducing mammography image noise, edge detection of breast cancer, clinical decision support in radiotherapy treatment, and cancer classification. Conclusion: These studies revealed that integrating quantum science with ML can significantly improve patient care and clinical outcomes. Future studies should explore the integration of QC and ML and the development of novel algorithms to enhance cancer prognosis, diagnosis, and treatment planning.
Keywords: cancer; machine learning; oncology; quantum computer; quantum machine learning.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting InterestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023;73(1):17‐48. - PubMed
-
- de Martel C, Georges D, Bray F, Ferlay J, Clifford GM. Global burden of cancer attributable to infections in 2018: A worldwide incidence analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2020;8(2):e180‐ee90. - PubMed
-
- Organization WH. Assessing national capacity for the prevention and control of noncommunicable diseases: report of the 2019 global survey. 2020.
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209‐249. - PubMed
-
- Mateo J, Steuten L, Aftimos P, et al. Delivering precision oncology to patients with cancer. Nat Med. 2022;28(4):658‐665. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical