Association of plasma biomarkers with cognition, cognitive decline, and daily function across and within neurodegenerative diseases: Results from the Ontario Neurodegenerative Disease Research Initiative
- PMID: 38105605
- PMCID: PMC10984487
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.13560
Association of plasma biomarkers with cognition, cognitive decline, and daily function across and within neurodegenerative diseases: Results from the Ontario Neurodegenerative Disease Research Initiative
Abstract
Introduction: We investigated whether novel plasma biomarkers are associated with cognition, cognitive decline, and functional independence in activities of daily living across and within neurodegenerative diseases.
Methods: Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), neurofilament light chain (NfL), phosphorylated tau (p-tau)181 and amyloid beta (Aβ)42/40 were measured using ultra-sensitive Simoa immunoassays in 44 healthy controls and 480 participants diagnosed with Alzheimer's disease/mild cognitive impairment (AD/MCI), Parkinson's disease (PD), frontotemporal dementia (FTD) spectrum disorders, or cerebrovascular disease (CVD).
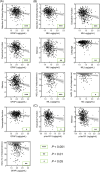
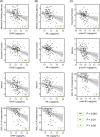
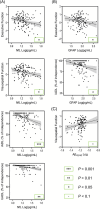
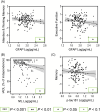
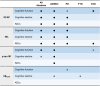
Results: GFAP, NfL, and/or p-tau181 were elevated among all diseases compared to controls, and were broadly associated with worse baseline cognitive performance, greater cognitive decline, and/or lower functional independence. While GFAP, NfL, and p-tau181 were highly predictive across diseases, p-tau181 was more specific to the AD/MCI cohort. Sparse associations were found in the FTD and CVD cohorts and for Aβ42/40 .
Discussion: GFAP, NfL, and p-tau181 are valuable predictors of cognition and function across common neurodegenerative diseases, and may be useful in specialized clinics and clinical trials.
Keywords: activities of daily living; amyloid; amyloid beta; blood; blood-based; cognition; dementia; glial fibrillary acidic protein; longitudinal; neurofilament light chain; neuropsychiatric; phosphorylated tau; protein; tau; vascular.
© 2023 The Authors. Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
H.Z. has served on scientific advisory boards and/or as a consultant for Abbvie, Acumen, Alector, Alzinova, ALZPath, Annexon, Apellis, Artery Therapeutics, AZTherapies, CogRx, Denali, Eisai, Nervgen, Novo Nordisk, Optoceutics, Passage Bio, Pinteon Therapeutics, Prothena, Red Abbey Labs, reMYND, Roche, Samumed, Siemens Healthineers, Triplet Therapeutics, and Wave; has given lectures in symposia sponsored by Cellectricon, Fujirebio, Alzecure, Biogen, and Roche; and is a co‐founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program (outside submitted work). D.A.G. has received honorarium for speaking from Ipsen, and honorarium for consulting from Allergan and Abbvie. M.F. is listed on a patent related to methods and kits for differential diagnosis of Alzheimer disease versus frontotemporal dementia using blood biomarkers. M.B. received royalties/licenses from Roche, and consulting fees from Biogen. RHS reports ownership in FollowMD Inc., a vascular risk reduction clinic. T.K.R. participated in 2021 and 2022 in an advisory activity for Biogen Canada Inc. T.K.R. is also an inventor on the United States Provisional Patent No. 17/396,030 that describes cell‐based assays and kits for assessing serum cholinergic receptor activity. Unrelated to this work, M.M. reports personal fees from Henry Stewart Talks, Alector, Biogen Canada, and Wave Life Sciences; as well as grants from Roche, Alector and Washington University. E.S., T.W., G.C., S.M., A.A.B., J.R., M.A.B., S.E.B., A.A.D., R.A.D., D.D., S.F., E.F., C.E.F., A.F., R.A.G., A.H., R.A.H., S.K., A.E.L., C.M., P.M.M., J.B.O., S.H.P., B.G.P., A.C.R., J.F.R., E.R., D.J.S., G.S., M.J.S., D.F.T., M.C.T., A.K.T., H.K., and D.P.M. report no conflicts. Author disclosures are available in the supporting information.
Figures
References
-
- Prince MJ, Wimo A, Guerchet MM, Ali GC, Wu Y‐T, Prina M, World Alzheimer Report 2015 ‐ The Global Impact of Dementia. London: Alzheimer's Disease International; 2015.
-
- Karikari TK, Pascoal TA, Ashton NJ, et al. Blood phosphorylated tau 181 as a biomarker for Alzheimer's disease: a diagnostic performance and prediction modelling study using data from four prospective cohorts. The Lancet Neurology. 2020;19:422‐433. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

