This is a preprint.
A complex of the lipid transport ER proteins TMEM24 and C2CD2 with band 4.1 at cell-cell contacts
- PMID: 38106008
- PMCID: PMC10723409
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.12.06.570396
A complex of the lipid transport ER proteins TMEM24 and C2CD2 with band 4.1 at cell-cell contacts
Update in
-
A complex of the lipid transport ER proteins TMEM24 and C2CD2 with band 4.1 at cell-cell contacts.J Cell Biol. 2024 Nov 4;223(11):e202311137. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202311137. Epub 2024 Aug 19. J Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 39158698 Free PMC article.
Abstract
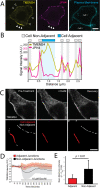
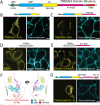
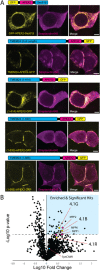
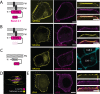
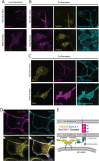
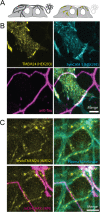
Junctions between the ER and the plasma membrane (ER/PM junctions) are implicated in calcium homeostasis, non-vesicular lipid transfer and other cellular functions. Two ER proteins that function both as membrane tethers to the PM via a polybasic motif in their C-terminus and as phospholipid transporters are brain-enriched TMEM24 (C2CD2L) and its paralog C2CD2. Based on an unbiased proximity ligation analysis, we found that both proteins can also form a complex with band 4.1 family members, which in turn can bind a variety of plasma membrane proteins including cell adhesion molecules such as SynCAM 1. This complex results in the enrichment of TMEM24 and C2CD2 containing ER/PM junctions at sites of cell contacts. Dynamic properties of TMEM24-dependent ER/PM contacts are impacted when in complex as TMEM24 present at cell adjacent junctions is not shed by calcium rise, unlike TMEM24 at non-cell adjacent junctions. These findings suggest that cell-contact interactions control ER/PM junctions via TMEM24 complexes involving band 4.1 proteins.
Figures

References
-
- Baines A.J., Lu H.-C., and Bennett P.M.. 2014. The Protein 4.1 family: Hub proteins in animals for organizing membrane proteins. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes. 1838:605–619. - PubMed
-
- Bharathan N.K., Giang W., Hoffman C.L., Aaron J.S., Khuon S., Chew T.-L., Preibisch S., Trautman E.T., Heinrich L., Bogovic J., Bennett D., Ackerman D., Park W., Petruncio A., Weigel A.V., Saalfeld S., Wayne Vogl A., Stahley S.N., and Kowalczyk A.P.. 2023. Architecture and dynamics of a desmosome–endoplasmic reticulum complex. Nature Cell Biology. 25:823–835. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Biederer T., Sara Y., Mozhayeva M., Atasoy D., Liu X., Kavalali E.T., and Südhof T.C.. 2002. SynCAM, a Synaptic Adhesion Molecule That Drives Synapse Assembly. Science. 297:1525–1531. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
