Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Explore the Mechanism of Mubiezi-Yinyanghuo Herb Pair in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 38106514
- PMCID: PMC10723923
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/4502994
Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Explore the Mechanism of Mubiezi-Yinyanghuo Herb Pair in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
Objective: Our previous studies have shown that the Mubiezi-Yinyanghuo (MBZ-YYH) herb pair inhibits rheumatoid arthritis (RA) cell proliferation and glycolysis, promising results with an obscure mechanism of action.
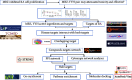
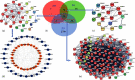
Methods: Therefore, it is necessary to explore the main components of MBZ-YYH and unravel the potential mechanism in RA based on network pharmacology and molecular docking methods. Components and targets of MBZ-YYH were retrieved from the TCMSP. Relevant targets of RA were searched in GeneCards, therapeutic target database (TTD), and DisGeNET databases; the common targets of the MBZ-YYH compounds and RA were obtained by comparison; and a component-target interaction network was established by Cytoscape 3.9.1. Gene ontology (GO) analysis and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Gene and Genome (KEGG) pathway enrichment analysis were performed through the David database. Molecular docking was performed by PyMoL2.3.0 and AutoDock Vina1.1.2 software.
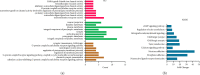
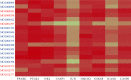
Results: 7 active ingredients and 58 putatively identified target genes were screened from MBZ, and 16 effective components of YYH and 230 potential targets were identified. There were 29 mutual targets between the two herbs and RA. Through the PPI network, 9 hub targets which contain JUN, CASP3, PPARG, PTGS2, GSK3B, CASP8, HMOX1, ICAM1, and HK2 were screened out. GO term enrichment analysis indicated that positive regulation of the apoptotic process, response to drugs, and response to hypoxia were significantly enriched. Based on KEGG analysis, it was mainly associated with the IL-17 signaling pathway, the TNF signaling pathway, and the p53 signaling pathway. The docking analysis revealed that the effective components showed strong binding activity with the receptors.
Conclusion: The effects of the MBZ-YYH herb pair on RA were coordinated by the interaction of diverse components, which may be through the IL-17 signaling pathway and the TNF signaling pathway, which target GSK3B, HK2, caspase 3, and caspase 8, inhibiting the proliferation and glycolysis of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synovial cells (RA-FLS) and tending towards an increasing efficacy and decreasing toxicity effect on RA.
Copyright © 2023 Fuxue Meng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
[Anti-rheumatoid arthritis mechanism of Sophorae Tonkinesis Radix et Rhizoma based on network pharmacology and experimental verification].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022 Oct;47(19):5327-5335. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20220526.401. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 36472040 Chinese.
-
Exploring the active ingredients and potential mechanisms of action of sinomenium acutum in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis based on systems biology and network pharmacology.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Feb 27;10:1065171. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1065171. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 36923645 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of Tripterygium wilfordii Hook.F.- Trichosanthes kirilowii Maxim decoction in treatment of diabetic kidney disease based on network pharmacology and molecular docking.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 28;13:940773. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.940773. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36386135 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Targets and Mechanisms of Scutellariae radix-Coptidis rhizoma Drug Pair for the Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Jun 4;2021:9929093. doi: 10.1155/2021/9929093. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34149863 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of the mechanism of Zisheng Shenqi decoction against gout arthritis using network pharmacology.Comput Biol Chem. 2021 Feb;90:107358. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2020.107358. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Comput Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33243703 Review.
References
-
- Wang R. H., Dai X. J., Wu H., et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of geniposide on regulating the functions of rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts via inhibiting sphingosine-1-phosphate receptors1/3 coupling gαi/gαs conversion. Frontiers in Pharmacology . 2020;11 doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.584176.584176 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

