Voclosporin and the Antiviral Effect Against SARS-CoV-2 in Immunocompromised Kidney Patients
- PMID: 38106593
- PMCID: PMC10719564
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ekir.2023.09.003
Voclosporin and the Antiviral Effect Against SARS-CoV-2 in Immunocompromised Kidney Patients
Abstract
Introduction: Immunocompromised kidney patients are at increased risk of prolonged SARS-CoV-2 infection and related complications. Preclinical evidence demonstrates a more potent inhibitory effect of voclosporin on SARS-CoV-2 replication than tacrolimus in vitro. We investigated the potential antiviral effects of voclosporin on SARS-CoV-2 in immunocompromised patients.
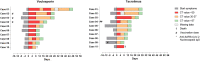
Methods: First, we conducted a prospective, randomized, open-label, proof-of-concept study in 20 kidney transplant recipients (KTRs) on tacrolimus-based immunosuppression who contracted mild to moderate SARS-CoV-2 infection. Patients were randomized to continue tacrolimus or switch to voclosporin. Second, we performed a post hoc analysis on SARS-CoV-2 infections in 216 patients with lupus nephritis (LN) on standard immunosuppression who were randomly exposed to voclosporin or placebo as part of a clinical trial that was conducted during the worldwide COVID-19 pandemic.
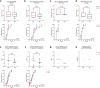
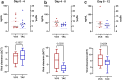
Results: The primary end point was clearance of SARS-CoV-2 viral load and that did not differ between voclosporin-treated KTRs (median 12 days, interquartile range [IQR] 8-28) and tacrolimus-treated KTRs (median 12 days, IQR 4-16) nor was there a difference in clinical recovery. Pharmacokinetic analyses demonstrated that, when voclosporin trough levels were on-target, SARS-CoV-2 viral load dropped significantly more (ΔCt 7.7 [3.4-10.7]) compared to tacrolimus-treated KTRs (ΔCt 2.7 [2.0-4.3]; P = 0.035). In voclosporin-exposed patients with LN, SARS-CoV-2 infection was detected in 6% (7/116) compared to 12% (12/100) in placebo-exposed patients (relative risk [RR] 1.4 [0.97-2.06]). Notably, no voclosporin-exposed patients with LN died from severe SARS-CoV-2 infection compared to 3% (3/100) in placebo-exposed patients (RR 2.2 [1.90-2.54]).
Conclusion: This proof-of-concept study shows a potential positive risk-benefit profile for voclosporin in immunocompromised patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection. These results warrant further investigations on voclosporin to establish an equipoise between infection and maintenance immunosuppression.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; calcineurin inhibitors; kidney transplantation; lupus erythematosus; lupus nephritis.
© 2023 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

