Hydrogen peroxide as a mitigation against Microcystis sp. bloom
- PMID: 38106988
- PMCID: PMC10518459
- DOI: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2023.739932
Hydrogen peroxide as a mitigation against Microcystis sp. bloom
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Hydrogen peroxide as a mitigation against Microcystis sp. Bloom" [Aquaculture, Volume 577, 15 December 2023, 739932].Aquaculture. 2025 Jan 30;595:741655. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2024.741655. Aquaculture. 2025. PMID: 39886098 Free PMC article.
Abstract
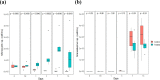
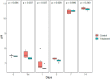
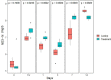
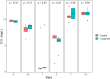
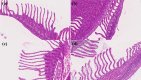
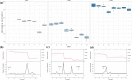
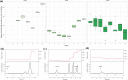
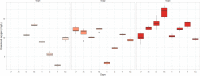
Microcystis sp. is a harmful cyanobacterial species commonly seen in earthen ponds. The overgrowth of these algae can lead to fluctuations in water parameters, including DO and pH. Also, the microcystins produced by these algae are toxic to aquatic animals. This study applied hydrogen peroxide (7 mg/L) to treat Microcystis sp. in a laboratory setting and in three earthen pond trials. In the lab we observed a 64.7% decline in Microcystis sp. And in our earthen pond field experiments we measured, on average, 43% reductions in Microcystis sp. cell counts within one hour. The treatment was found to eliminate specifically Microcystis sp. and did not reduce the cell count of the other algae species in the pond. A shift of the algae community towards the beneficial algae was also found post-treatment. Lastly, during the pond trials, the gill status of Tilapia and Giant tiger prawn were not affected by the H2O2 treatment suggesting this may be a good mitigation strategy for reducing cyanobacteria in pond aquaculture.
Keywords: Aquaculture; Harmful algal bloom; Hydrogen peroxide; Pond water.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: POK HIM NG reports financial support and equipment, drugs, or supplies were provided by Agriculture, Fisheries and Conservation Department (AFCD), Hong Kong SAR, China.
Figures






References
-
- Al Shehhi M.R., Gherboudj I., Ghedira H. An overview of historical harmful algae blooms outbreaks in the Arabian seas. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014;86(1–2):314–324. - PubMed
-
- Arvin E., Pedersen L.-F. Hydrogen peroxide decomposition kinetics in aquaculture water. Aquac. Eng. 2015;64:1–7.
-
- Balaji-Prasath B., Wang Y., Su Y.P., Hamilton D.P., Lin H., Zheng L., Zhang Y. Methods to control harmful algal blooms: a review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022:1–20. - PubMed
-
- Belfiore A.P., Buley R.P., Fernandez-Figueroa E.G., Gladfelter M.F., Wilson A.E. Zooplankton as an alternative method for controlling phytoplankton in catfish pond aquaculture. Aquac. Rep. 2021;21
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
