Steps to achieve carvone-rich spearmint (Mentha spicata L.) essential oil: a case study on the use of different distillation methods
- PMID: 38107005
- PMCID: PMC10722908
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1292224
Steps to achieve carvone-rich spearmint (Mentha spicata L.) essential oil: a case study on the use of different distillation methods
Abstract
Introduction: Spearmint essential oil is a valuable medical and food product. Spearmint essential oil is effective for the treatment of flatulence, indigestion, nausea, and colic along with Alzheimer, obesity, and fungal infections.
Methods: This study evaluated the quality and quantity of spearmint essential oil by examining some extraction strategies. The procedures were hydro-distillation, hydro-steam distillation, microwave-assisted hydro-distillation, and open hydro-distillation. The hydro-distillation had five pH levels (2, 4, 6, 8, and 10) and four NaCl concentrations (0.5, 1, 1.5, and 2%). microwave-assisted hydro-distillation at a power of 225 W was applied for 60, 90, and 120 minutes for process durations. The solvent extraction of herbal distillate obtained by an open hydro-distillation system was done using n-pentane and n-hexane to achieve a recovered essential oil by a rotary evaporator.
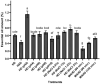
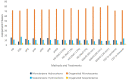
Results and discussion: The results showed that the lowest pH in the hydro-distillation process led to obtaining double yield compared to the control. Additionally, at 1 and 1.5% NaCl concentrations, the oil yield increased by 12.86 and 20.87%, respectively. Although the yield was reduced by microwave-assisted hydro-distillation, however within 120 minutes, carvone increased by 12.7% and limonene decreased by 42.3%. The best quality of spearmint oil belonged to solvent extraction followed by rotary evaporator.
Keywords: distillation; hydro-steam; microwave; solvent extraction; spearmint.
Copyright © 2023 Moradi-Sadr, Ebadi and Ayyari.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect of distillation waste water and plant hormones on spearmint growth and composition.J Sci Food Agric. 2011 Apr;91(6):1135-41. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.4297. Epub 2011 Feb 15. J Sci Food Agric. 2011. PMID: 21328358
-
Microwave-Assisted Hydro-Distillation of Essential Oil from Rosemary: Comparison with Traditional Distillation.Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2018 Jan-Mar;10(1):22-28. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29296263 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive Profile of Distilled Solid By-Products of Rosemary, Greek Sage and Spearmint as Affected by Distillation Methods.Molecules. 2022 Dec 19;27(24):9058. doi: 10.3390/molecules27249058. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36558189 Free PMC article.
-
Mentha spicata as natural analgesia for treatment of pain in osteoarthritis patients.Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2017 Feb;26:1-4. doi: 10.1016/j.ctcp.2016.11.001. Epub 2016 Nov 2. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2017. PMID: 28107842 Review.
-
Mentha spicata L. essential oil, phytochemistry and its effectiveness in flatulence.J Tradit Complement Med. 2018 Sep 28;11(2):75-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2017.08.011. eCollection 2021 Mar. J Tradit Complement Med. 2018. PMID: 33728265 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abdel-Hameed E.-S. S., Salman M. S., Fadl M. A., Elkhateeb A., El-Awady M. A. (2018). Chemical composition of hydrodistillation and solvent free microwave extraction of essential oils from Mentha piperita L. growing in Taif, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, and their anticancer and antimicrobial activity. Orient. J. Chem. 34, 222. doi: 10.13005/ojc/340125 - DOI
-
- Adams R. P. (2007). Identification of essential oil components by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (IL: Allured publishing corporation Carol Stream; ).
-
- Ali-Shtayeh M. S., Jamous R. M., Abu-Zaitoun S. Y., Khasati A. I., Kalbouneh S. R. (2019). Biological properties and bioactive components of Mentha spicata L. essential Oil: focus on potential benefits in the treatment of obesity, Alzheimer’s Disease, Dermatophytosis, and Drug-Resistant Infections. Evidence-Based Complement. Altern. Med 2019. doi: 10.1155/2019/3834265 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Babu G. D. K., Singh B. (2010). Characteristics variation of lavender oil produced by different hydrodistillation techniques. Compr. Bioact. Nat. Prod. Qual. Control Stand. 8, 122–136.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

