Update of the Xylella spp. host plant database - systematic literature search up to 30 June 2023
- PMID: 38107375
- PMCID: PMC10722330
- DOI: 10.2903/j.efsa.2023.8477
Update of the Xylella spp. host plant database - systematic literature search up to 30 June 2023
Abstract
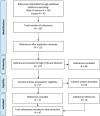
This scientific report provides an update of the Xylella spp. host plant database, aiming to provide information and scientific support to risk assessors, risk managers and researchers dealing with Xylella spp. Upon a mandate of the European Commission, EFSA created and regularly updates a database of host plant species of Xylella spp. The current mandate covers the period 2021-2026. This report is related to the ninth version of the database published in Zenodo in the EFSA Knowledge Junction community, covering literature published from 1 January 2023 up to 30 June 2023, and recent Europhyt outbreak notifications. Informative data have been extracted from 47 selected publications. Seven new host plants were identified and added to the database. These plant species were naturally infected by X. fastidiosa subsp. multiplex in France, Spain and the United States. No additional data were retrieved for X. taiwanensis, and no additional multilocus sequence tipes (STs) were identified worldwide. New information on the tolerant/resistant response of plant species to X. fastidiosa infection were added to the database. The Xylella spp. host plant species were listed in different categories based on the number and type of detection methods applied for each finding. The overall number of Xylella spp. host plants determined with at least two different detection methods or positive with one method (between sequencing and pure culture isolation (category A), reaches now 439 plant species, 200 genera and 69 families. Such numbers rise to 696 plant species, 307 genera and 88 families if considered regardless of the detection methods applied (category E).
Keywords: Xylella fastidiosa; Xylella spp.; data extraction; database; host plants; sequence types; subspecies.
© 2023 European Food Safety Authority. EFSA Journal published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH on behalf of European Food Safety Authority.
Conflict of interest statement
If you wish to access the declaration of interests of any expert contributing to an EFSA scientific assessment, please contact interestmanagement@efsa.europa.eu.
Figures

References
-
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) . (2010). Application of systematic review methodology to food and feed safety assessments to support decision making. EFSA Journal, 8(6), 1637. 10.2903/j.efsa.2010.1637 - DOI
-
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) . (2016). Update of a database of host plants of Xylella fastidiosa: 20 November 2015. EFSA Journal, 14(2), 4378. 10.2903/j.efsa.2016.4378 - DOI
-
- EPPO (European and Mediterranean Plant Protection Organization) . (2023). EPPO global database. https://gd.eppo.int
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
