Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase interactions in SARS-CoV-2 infection
- PMID: 38108455
- PMCID: PMC10754286
- DOI: 10.1042/BST20230527
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase interactions in SARS-CoV-2 infection
Abstract
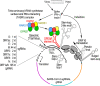
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (aaRSs) are ancient enzymes that serve a foundational role in the efficient and accurate translation of genetic information from messenger RNA to proteins. These proteins play critical, non-canonical functions in a multitude of cellular processes. Multiple viruses are known to hijack the functions of aaRSs for proviral outcomes, while cells modify antiviral responses through non-canonical functions of certain synthetases. Recent findings have revealed that severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the etiological agent of coronaviral disease 19 (COVID-19), utilizes canonical and non-canonical functions of aaRSs, establishing a complex interplay of viral proteins, cellular factors and host aaRSs. In a striking example, an unconventional multi-aaRS complex consisting of glutamyl-prolyl-, lysyl-, arginyl- and methionyl-tRNA synthetases interact with a previously unknown RNA-element in the 3'-end of SARS-CoV-2 genomic and subgenomic RNAs. This review aims to highlight the aaRS-SARS-CoV-2 interactions identified to date, with possible implications for the biology of host aaRSs in SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Keywords: RNA virus; SARS-COV-2; UTR; aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase; post-transcriptional region.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

