Oral Metformin Inhibits Choroidal Neovascularization by Modulating the Gut-Retina Axis
- PMID: 38108689
- PMCID: PMC10732090
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.64.15.21
Oral Metformin Inhibits Choroidal Neovascularization by Modulating the Gut-Retina Axis
Abstract
Purpose: Emerging data indicate that metformin may prevent the development of age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Whereas the underlying mechanisms of metformin's anti-aging properties remain undetermined, one proposed avenue is the gut microbiome. Using the laser-induced choroidal neovascularization (CNV) model, we investigate the effects of oral metformin on CNV, retinal pigment epithelium (RPE)/choroid transcriptome, and gut microbiota.
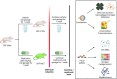
Methods: Specific pathogen free (SPF) male mice were treated via daily oral gavage of metformin 300 mg/kg or vehicle. Male mice were selected to minimize sex-specific differences to laser induction and response to metformin. Laser-induced CNV size and macrophage/microglial infiltration were assessed by isolectin and Iba1 immunostaining. High-throughput RNA-seq of the RPE/choroid was performed using Illumina. Fecal pellets were analyzed for gut microbiota composition/pathways with 16S rRNA sequencing/shotgun metagenomics, as well as microbial-derived metabolites, including small-chain fatty acids and bile acids. Investigation was repeated in metformin-treated germ-free (GF) mice and antibiotic-treated/GF mice receiving fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) from metformin-treated SPF mice.
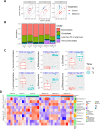
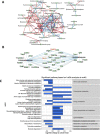
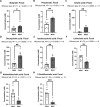
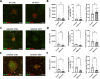
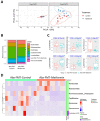
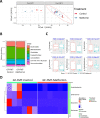
Results: Metformin treatment reduced CNV size (P < 0.01) and decreased Iba1+ macrophage/microglial infiltration (P < 0.005). One hundred forty-five differentially expressed genes were identified in the metformin-treated group (P < 0.05) with a downregulation in pro-angiogenic genes Tie1, Pgf, and Gata2. Furthermore, metformin altered the gut microbiome in favor of Bifidobacterium and Akkermansia, with a significant increase in fecal levels of butyrate, succinate, and cholic acid. Metformin did not suppress CNV in GF mice but colonization of microbiome-depleted mice with metformin-derived FMT suppressed CNV.
Conclusions: These data suggest that oral metformin suppresses CNV, the hallmark lesion of advanced neovascular AMD, via gut microbiome modulation.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures


References
-
- Wong WL, Su X, Li X, et al.. Global prevalence of age-related macular degeneration and disease burden projection for 2020 and 2040: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2014; 2(2): e106–e116. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

