The Role of Early Treatment in the Management of Axial Spondyloarthritis: Challenges and Opportunities
- PMID: 38108992
- PMCID: PMC10796311
- DOI: 10.1007/s40744-023-00627-0
The Role of Early Treatment in the Management of Axial Spondyloarthritis: Challenges and Opportunities
Abstract
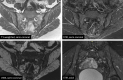
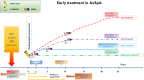
Axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) is a chronic, inflammatory rheumatic disease that primarily affects the axial skeleton, often inflicting severe pain, diminished mobility, and a compromised quality of life. The advent of Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society (ASAS) classification criteria for spondyloarthritis (SpA) have enabled the classification of patients with axSpA in the non-radiographic stage but poorly perform if mistakenly used for diagnostic purposes. Despite notable progress in early diagnosis facilitated by referral strategies and extensive magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) utilization, diagnostic delays persist as a concerning issue. This underscores the urgency to narrow the diagnostic gap and highlights the critical role of early diagnosis in mitigating the long-term structural damage associated with this condition. Research into the impact of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) on inflammatory symptoms and radiographic progression has been extensive. A compelling body of evidence suggests that early intervention leads to superior disease outcomes. However, most of these studies have centered on patients with established diseases rather than those in the early stages. Consequently, findings from studies on early pharmacological intervention remain inconclusive, and the potential for modifying the disease trajectory is still debatable. Without precise data from clinical trials, insights from basic science regarding the pathogenic mechanisms might point toward potential targets that warrant early intervention in the disease process. This review underscores the urgency of early diagnosis and intervention in axSpA, highlighting ongoing research gaps and the need for further exploration to improve patient outcomes.
Keywords: Disease progression; Early axial spondyloarthritis; IL-17 pathway; TNF-alpha; Therapeutic intervention.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Denis Poddubnyy: Research support from AbbVie, Eli Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer; Consulting fees from AbbVie, Biocad, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Moonlake, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB; Speaker fees from AbbVie, Canon, DKSH, Eli Lilly, Janssen, MSD, Medscape, Novartis, Peervoice, Pfizer, and UCB; Member of the executive committee of ASAS; Member of steering committee of GRAPPA. Francesco Ciccia: Research support from AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer; Consulting and speaking fees from AbbVie, Astra Zeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB; Full member of ASAS. Daniele Mauro and Guilio Forte have nothing to disclose.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

