Lymphadenopathy in the rheumatology practice: a pragmatic approach
- PMID: 38109670
- PMCID: PMC11147542
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/kead644
Lymphadenopathy in the rheumatology practice: a pragmatic approach
Abstract
Lymphadenopathy is a common clinical finding and diagnostic challenge within general medicine and rheumatology practice. It may represent a primary manifestation of an underlying immune-mediated disease or indicate an infectious or neoplastic complication requiring differing management. Evaluating lymphadenopathy is of particular relevance in rheumatology, given that lymph node enlargement is a common finding within the clinical spectrum of several well-known rheumatologic disorders including RA, SLE and SS. In addition, lymphadenopathy represents a hallmark manifestation of rare immunological diseases such as Castleman disease and IgG4-related disease that must be considered in the differential diagnosis because effective targeted treatments can now impact the prognosis of these conditions. In this review we present an overview of the clinical significance of lymphadenopathy in common and rare rheumatologic diseases and propose a practical approach to lymphadenopathy in the rheumatology practice. Differential diagnosis of Castleman disease and therapeutic options for this condition of increasing rheumatologic interest will be discussed in detail.
Keywords: Castleman disease; IgG4-related disease; arthritis; connective tissue disease; lymph node enlargement; sarcoidosis; siltuximab.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology.
Figures
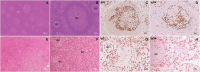
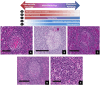

Comment in
-
Comment on: Lymphadenopathy in the rheumatology practice: a pragmatic approach.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2024 May 3;63(6):e193-e194. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keae151. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2024. PMID: 38460186 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lawley TJ, Bielory L, Gascon P et al. A prospective clinical and immunologic analysis of patients with serum sickness. N Engl J Med 1984;311:1407–13. - PubMed
-
- Karmacharya P, Poudel DR, Pathak R et al. Rituximab-induced serum sickness: a systematic review. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2015;45:334–40. - PubMed
-
- Clark BM, Kotti GH, Shah AD, Conger NG. Severe serum sickness reaction to oral and intramuscular penicillin. Pharmacotherapy 2006;26:705–8. - PubMed
-
- Misirlioglu ED, Duman H, Ozmen S, Bostanci I. Serum sickness-like reaction in children due to cefditoren. Pediatr Dermatol 2012;29:327–8. - PubMed

