Effects of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor on Experimental Diabetic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 38109999
- PMCID: PMC10922867
- DOI: 10.1016/j.labinv.2023.100305
Effects of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor on Experimental Diabetic Kidney Disease
Abstract
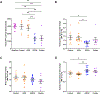
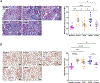
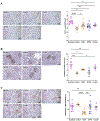
Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is the leading cause of end-stage kidney disease in the United States and worldwide. Proteinuria is a major marker of the severity of injury. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor (DPP-4I) increases incretin-related insulin production and is, therefore, used to treat diabetes. We investigated whether DPP4I could have direct effect on kidney independent of its hypoglycemic activity. We, therefore, tested the effects of DPP4I with or without angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEI) on the progression of diabetic nephropathy and albuminuria in a murine model of DKD. eNOS-/-db/db mice were randomized to the following groups at age 10 weeks and treated until sacrifice: baseline (sacrificed at week 10), untreated control, ACEI, DPP4I, and combination of DPP4I and ACEI (Combo, sacrificed at week 18). Systemic parameters and urine albumin-creatinine ratio were assessed at baseline, weeks 14, and 18. Kidney morphology, glomerular filtration rate (GFR), WT-1, a marker for differentiated podocytes, podoplanin, a marker of foot process integrity, glomerular collagen IV, and alpha-smooth muscle actin were assessed at the end of the study. All mice had hyperglycemia and proteinuria at study entry at week 10. Untreated control mice had increased albuminuria, progression of glomerular injury, and reduced GFR at week 18 compared with baseline. DPP4I alone reduced blood glucose and kidney DPP-4 activity but failed to protect against kidney injury compared with untreated control. ACEI alone and combination groups showed significantly reduced albuminuria and glomerular injury, and maintained GFR and WT-1+ cells. Only the combination group had significantly less glomerular collagen IV deposition and more podoplanin preservation than the untreated control. DPP-4I alone does not decrease the progression of kidney injury in the eNOS-/-db/db mouse model, suggesting that targeting only hyperglycemia is not an optimal treatment strategy for DKD. Combined DPP-4I with ACEI added more benefit to reducing the glomerular matrix.
Keywords: angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; diabetic kidney disease; dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor.
Copyright © 2023 United States & Canadian Academy of Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
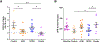
Similar articles
-
Blood pressure and glucose independent renoprotective effects of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibition in a mouse model of type-2 diabetic nephropathy.J Hypertens. 2014 Nov;32(11):2211-23; discussion 2223. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000000328. J Hypertens. 2014. PMID: 25215436
-
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibition in chronic kidney disease and potential for protection against diabetes-related renal injury.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2016 May;26(5):361-73. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2016.01.001. Epub 2016 Jan 13. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2016. PMID: 27105869 Review.
-
SGLT2 inhibitors: a novel choice for the combination therapy in diabetic kidney disease.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2017 May 16;16(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s12933-017-0547-1. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2017. PMID: 28511711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stromal cell-derived factor-1 is upregulated by dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibition and has protective roles in progressive diabetic nephropathy.Kidney Int. 2016 Oct;90(4):783-96. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2016.06.012. Epub 2016 Jul 27. Kidney Int. 2016. PMID: 27475229
-
Antiproteinuric effect of DPP-IV inhibitors in diabetic and non-diabetic kidney diseases.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Sep;159:105019. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105019. Epub 2020 Jun 15. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 32553713 Review.
Cited by
-
New Insights into the Pleiotropic Actions of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors Beyond Glycaemic Control.touchREV Endocrinol. 2024 Oct;20(2):19-29. doi: 10.17925/EE.2024.20.2.5. Epub 2024 Sep 6. touchREV Endocrinol. 2024. PMID: 39526061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The threshold effect of triglyceride glucose index on diabetic kidney disease risk in patients with type 2 diabetes: unveiling a non-linear association.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jun 13;15:1411486. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1411486. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38938513 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative effectiveness of combining antidiabetic medications to treat renal impairment in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 16;15(1):25735. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-10299-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40670474 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jung E, Kim J, Ho Kim S, et al. Gemigliptin improves renal function and attenuates podocyte injury in mice with diabetic nephropathy. Eur J Pharmacol 2015;761:116–124. - PubMed
-
- Ruggenenti P, Fassi A, Ilieva AP, et al. Preventing microalbuminuria in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2004;351:1941–1951. - PubMed
-
- Mogensen CE, Poulsen PL. Epidemiology of microalbuminuria in diabetes and in the background population. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 1994;3:248–256. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

