A Generic Antibody-Blocking Protein That Enables pH-Switchable Activation of Antibody Activity
- PMID: 38110237
- PMCID: PMC10804362
- DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.3c00449
A Generic Antibody-Blocking Protein That Enables pH-Switchable Activation of Antibody Activity
Abstract
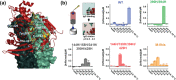
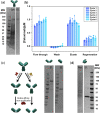
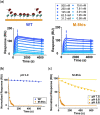
Molecular strategies that allow for reversible control of antibody activity have drawn considerable interest for both therapeutic and diagnostic applications. Protein M is a generic antibody-binding protein that binds to the Fv domain of IgGs and, in doing so, blocks antigen binding. However, the dissociation of protein M is essentially irreversible, which has precluded its use as an antibody affinity reagent and molecular mask to control antibody activity. Here, we show that introduction of 8 histidine residues on the Fv binding interface of protein M results in a variant that shows pH-switchable IgG binding. This protein M-8his variant provides an attractive and universal affinity resin for the purification of IgGs, antibody fragments (Fab and single-chain variable fragments (scFv)), and antibody conjugates. Moreover, protein M-8his enables the pH-dependent blocking of therapeutic antibodies, allowing the selective targeting of cells at pH 6.0.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of genetically-engineered antibodies.Q J Nucl Med. 1998 Dec;42(4):225-41. Q J Nucl Med. 1998. PMID: 9973838 Review.
-
Calcium-dependent affinity ligands for the purification of antibody fragments at neutral pH.J Chromatogr A. 2023 Apr 12;1694:463902. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2023.463902. Epub 2023 Feb 26. J Chromatogr A. 2023. PMID: 36871527
-
Applications for an engineered Protein-G variant with a pH controllable affinity to antibody fragments.J Immunol Methods. 2014 Dec 15;415:24-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2014.10.003. Epub 2014 Oct 22. J Immunol Methods. 2014. PMID: 25450256 Free PMC article.
-
Recognition of DNA by VH and Fv domains of an IgG anti-poly(dC) antibody with a singly mutated VH domain.J Mol Recognit. 2001 Jan-Feb;14(1):18-28. doi: 10.1002/1099-1352(200101/02)14:1<18::AID-JMR515>3.0.CO;2-2. J Mol Recognit. 2001. PMID: 11180559
-
Antibody Fragments as Tools for Elucidating Structure-Toxicity Relationships and for Diagnostic/Therapeutic Targeting of Neurotoxic Amyloid Oligomers.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 24;21(23):8920. doi: 10.3390/ijms21238920. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33255488 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Competition-Based Strategy for the Isolation of an Anti-Idiotypic Blocking Module and Fine-Tuning for Conditional Activation of a Therapeutic Antibody.Biotechnol J. 2024 Dec;19(12):e202400432. doi: 10.1002/biot.202400432. Biotechnol J. 2024. PMID: 39655405 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating molecular dynamics simulation with small- and wide-angle X-ray scattering to unravel the flexibility, antigen-blocking, and protease-restoring functions in a hindrance-based pro-antibody.Protein Sci. 2024 Sep;33(9):e5124. doi: 10.1002/pro.5124. Protein Sci. 2024. PMID: 39145427 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential of Single-Chain Variable Fragment Antibody: Role in Future Therapeutic and Diagnostic Biologics.J Immunol Res. 2024 Aug 9;2024:1804038. doi: 10.1155/2024/1804038. eCollection 2024. J Immunol Res. 2024. PMID: 39156005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Agglutination of yeast-binding antibodies from human blood plasma products.BMC Microbiol. 2025 Jul 29;25(1):457. doi: 10.1186/s12866-025-03989-3. BMC Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40730944 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Orozco C. T.; Bersellini M.; Irving L. M.; Howard W. W.; Hargreaves D.; Devine P. W. A.; Siouve E.; Browne G. J.; Bond N. J.; Phillips J. J.; Ravn P.; Jackson S. E. Mechanistic insights into the rational design of masked antibodies. MAbs 2022, 14, e209570110.1080/19420862.2022.2095701. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

