Proteomics-driven noninvasive screening of circulating serum protein panels for the early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 38110372
- PMCID: PMC10728065
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-44255-2
Proteomics-driven noninvasive screening of circulating serum protein panels for the early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
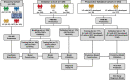
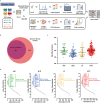
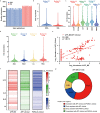
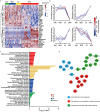
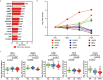
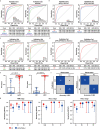
Early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) lacks highly sensitive and specific protein biomarkers. Here, we describe a staged mass spectrometry (MS)-based discovery-verification-validation proteomics workflow to explore serum proteomic biomarkers for HCC early diagnosis in 1002 individuals. Machine learning model determined as P4 panel (HABP2, CD163, AFP and PIVKA-II) clearly distinguish HCC from liver cirrhosis (LC, AUC 0.979, sensitivity 0.925, specificity 0.915) and healthy individuals (HC, AUC 0.992, sensitivity 0.975, specificity 1.000) in an independent validation cohort, outperforming existing clinical prediction strategies. Furthermore, the P4 panel can accurately predict LC to HCC conversion (AUC 0.890, sensitivity 0.909, specificity 0.877) with predicting HCC at a median of 11.4 months prior to imaging in prospective external validation cohorts (No.: Keshen 2018_005_02 and NCT03588442). These results suggest that proteomics-driven serum biomarker discovery provides a valuable reference for the liquid biopsy, and has great potential to improve early diagnosis of HCC.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- General Office of National Health Commission Standard for diagnosis and treatment of primary liver cancer (2022 edition) J. Clin. Hepatol. 2022;38:288–303. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.02.009. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

