Potent latency reversal by Tat RNA-containing nanoparticle enables multi-omic analysis of the HIV-1 reservoir
- PMID: 38110433
- PMCID: PMC10728105
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-44020-5
Potent latency reversal by Tat RNA-containing nanoparticle enables multi-omic analysis of the HIV-1 reservoir
Abstract
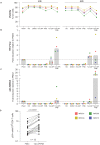
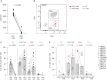
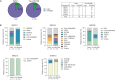
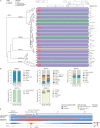
The development of latency reversing agents that potently reactivate HIV without inducing global T cell activation would benefit the field of HIV reservoir research and could pave the way to a functional cure. Here, we explore the reactivation capacity of a lipid nanoparticle containing Tat mRNA (Tat-LNP) in CD4 T cells from people living with HIV undergoing antiretroviral therapy (ART). When combined with panobinostat, Tat-LNP induces latency reversal in a significantly higher proportion of latently infected cells compared to PMA/ionomycin (≈ 4-fold higher). We demonstrate that Tat-LNP does not alter the transcriptome of CD4 T cells, enabling the characterization of latently infected cells in their near-native state. Upon latency reversal, we identify transcriptomic differences between infected cells carrying an inducible provirus and non-infected cells (e.g. LINC02964, GZMA, CCL5). We confirm the transcriptomic differences at the protein level and provide evidence that the long non-coding RNA LINC02964 plays a role in active HIV infection. Furthermore, p24+ cells exhibit heightened PI3K/Akt signaling, along with downregulation of protein translation, suggesting that HIV-infected cells display distinct signatures facilitating their long-term persistence. Tat-LNP represents a valuable research tool for in vitro reservoir studies as it greatly facilitates the in-depth characterization of HIV reservoir cells' transcriptome and proteome profiles.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors M.P., B.C., L.L., W.V.S., S.R., Y.N., N.D.L., A.D. and L.V.D. declare no competing interests. The authors E.V.G., E.N., F.E. and D.B. declare the following competing interests: these authors are employees of Johnson & Johnson and may be Johnson & Johnson, stockholders. The author J.V. declares the following competing interests: this author was an employee of Arcturus Therapeutics and may be an Arcturus Therapeutics stockholder.
Figures

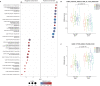
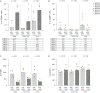
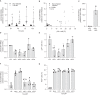
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

