Genetically predicted 486 blood metabolites concerning risk of systemic lupus erythematosus: a Mendelian randomization study
- PMID: 38110541
- PMCID: PMC10728112
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-49233-8
Genetically predicted 486 blood metabolites concerning risk of systemic lupus erythematosus: a Mendelian randomization study
Abstract
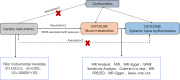
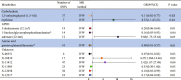
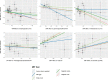
Metabolic abnormalities constitute a significant characteristic of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). We utilised a two-sample Mendelian randomisation (MR) study to evaluate the potential causal association between 486 blood metabolites and SLE. Exposure data at the metabolite level were extracted from 7824 European Genome-wide association studies (GWAS). Preliminary analysis utilised SLE GWAS data from FinnGen. The primary method for causal analysis relied on random inverse variance weighting (IVW). To ensure robustness, sensitivity analyses included the Cochran Q test, MR-Egger intercept test, MR-PRESSO, and leave-one-out analysis. Steiger testing and linkage disequilibrium score regression were employed to validate the identified metabolites. This study identified 12 metabolites, comprising six known chemical structures: 1,5-anhydroglucitol(1,5-AG) [odds ratio (OR) = 0.100, 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.015-0.773, P = 0.027), gamma-glutamylthreonine (OR = 0.077, 95% CI: 0.010-0.574, P = 0.012), 5-dodecenoate(12:1n7) (OR = 0.205, 95% CI: 0.061-0.685, P = 0.010), linoleoylglycerophosphoethanolamine * (OR = 0.159, 95% CI: 0.027-0.933, P = 0.044), erythrose (OR = 88.331,95% CI:1.098-63.214, P = 0.040) and 1-, adrenate (22:4n6) (OR = 9.876, 95% CI: 1.753-55.639, P = 0.001)]. Additionally, we found associations between SLE and six unknown chemical structures: X-06351 (OR = 0.071, 95% CI: 0.006-0.817, P = 0.034), X-10810 (OR = 4.268 95% CI: 1.260-14.459, P = 0.020), X-11412 (OR = 5.418 95% CI: 1.068-27.487, P = 0.041), X-11905 (OR = 0.551, 95%CI: 0.304-0.997, P = 0.049), X-12038 (OR = 0.178 95%CI: 0.032-0.988, P = 0.045), X-12217 (OR = 0.174 95%CI: 0.044-0.680, P = 0.014). This study offers evidence supporting a causal relationship between SLE and 12 circulating metabolites, six of which have known chemical structures and six that remain unidentified. These findings introduce a new perspective for further exploration of SLE mechanisms.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical