Evaluation and Application of a PET Tracer in Preclinical and Phase 1 Studies to Determine the Brain Biodistribution of Minzasolmin (UCB0599)
- PMID: 38110790
- PMCID: PMC10973027
- DOI: 10.1007/s11307-023-01878-7
Evaluation and Application of a PET Tracer in Preclinical and Phase 1 Studies to Determine the Brain Biodistribution of Minzasolmin (UCB0599)
Abstract
Purpose: Minzasolmin (UCB0599) is an orally administered, small molecule inhibitor of ASYN misfolding in development as a potential disease-modifying therapy for Parkinson's disease. Here we describe the preclinical development of a radiolabeled tracer and results from a phase 1 study using the tracer to investigate the brain distribution of minzasolmin.
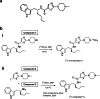
Procedures: In the preclinical study, two radiolabeling positions were investigated on the S-enantiomer of minzasolmin (UCB2713): [11C]methylamine UCB2713 ([11C-N-CH3]UCB2713) and [11C]carbonyl UCB2713 ([11C-CO]UCB2713). Male C57 black 6 mice (N = 10) received intravenous [11C-N-CH3]UCB2713; brain homogenates were assessed for radioactivity and plasma samples analyzed by high-performance liquid chromatography. Positron emission tomography-computed tomography (PET-CT) was used to image brains in a subset of mice (n = 3). In the open-label, phase 1 study, healthy volunteers were scanned twice with PET-CT following injection with [11C]minzasolmin radiotracer (≤ 10 µg), first without, then with oral dosing with non-radiolabeled minzasolmin 360 mg.
Primary objective: to determine biodistribution of minzasolmin in the human brain; secondary objectives included minzasolmin safety/tolerability.
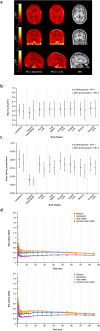
Results: Preclinical data supported the use of [11C]minzasolmin in clinical studies. In the phase 1 study, PET data showed substantial drug signal in the brain of healthy volunteers (N = 4). The mean estimated whole brain total distribution volume (VT) at equilibrium across all regions of interest was 0.512 mL/cm3, no difference in VT was observed following administration of minzasolmin 360 mg. Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were reported by 75% (n = 3) of participants. No drug-related TEAEs, deaths, serious adverse events, or discontinuations were reported.
Conclusion: Following positive preclinical results with the N-methyl labeled PET tracer, [11C]minzasolmin was used in the phase 1 study, which demonstrated that minzasolmin readily crossed the blood-brain barrier and was well distributed throughout the brain. Safety and pharmacokinetic findings were consistent with previous early-phase studies (such as UP0077, NCT04875962).
Keywords: Alpha-synuclein; Brain distribution; Minzasolmin; PET tracers; PET-imaging; Parkinson’s disease; Phase 1 study.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
RPM, JM, AOC, FXM, RN, and MW are all employees of UCB Pharma and may hold or have access to stock options. MB, ML, MG, JWS, and CO were employees of UCB Pharma at the time this work was conducted and may hold or have access to stock options. CP, MH, and GS are all employees of Invicro. VVA is an independent consultant.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

