Cellular and subcellular localization of Rab10 and phospho-T73 Rab10 in the mouse and human brain
- PMID: 38110990
- PMCID: PMC10726543
- DOI: 10.1186/s40478-023-01704-9
Cellular and subcellular localization of Rab10 and phospho-T73 Rab10 in the mouse and human brain
Abstract
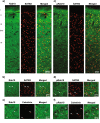
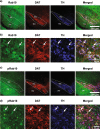
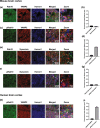
Autosomal dominant pathogenic mutations in Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) cause Parkinson's disease (PD). The most common mutation, G2019S-LRRK2, increases the kinase activity of LRRK2 causing hyper-phosphorylation of its substrates. One of these substrates, Rab10, is phosphorylated at a conserved Thr73 residue (pRab10), and is one of the most abundant LRRK2 Rab GTPases expressed in various tissues. The involvement of Rab10 in neurodegenerative disease, including both PD and Alzheimer's disease makes pinpointing the cellular and subcellular localization of Rab10 and pRab10 in the brain an important step in understanding its functional role, and how post-translational modifications could impact function. To establish the specificity of antibodies to the phosphorylated form of Rab10 (pRab10), Rab10 specific antisense oligonucleotides were intraventricularly injected into the brains of mice. Further, Rab10 knock out induced neurons, differentiated from human induced pluripotent stem cells were used to test the pRab10 antibody specificity. To amplify the weak immunofluorescence signal of pRab10, tyramide signal amplification was utilized. Rab10 and pRab10 were expressed in the cortex, striatum and the substantia nigra pars compacta. Immunofluorescence for pRab10 was increased in G2019S-LRRK2 knockin mice. Neurons, astrocytes, microglia and oligodendrocytes all showed Rab10 and pRab10 expression. While Rab10 colocalized with endoplasmic reticulum, lysosome and trans-Golgi network markers, pRab10 did not localize to these organelles. However, pRab10, did overlap with markers of the presynaptic terminal in both mouse and human cortex, including α-synuclein. Results from this study suggest Rab10 and pRab10 are expressed in all brain areas and cell types tested in this study, but pRab10 is enriched at the presynaptic terminal. As Rab10 is a LRRK2 kinase substrate, increased kinase activity of G2019S-LRRK2 in PD may affect Rab10 mediated membrane trafficking at the presynaptic terminal in neurons in disease.
Keywords: Antisense oligonucleotide; Mouse brain; Parkinson’s disease; Phosphorylation; Rab10; Rab10 knock down; pRab10.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
R1441G but not G2019S mutation enhances LRRK2 mediated Rab10 phosphorylation in human peripheral blood neutrophils.Acta Neuropathol. 2021 Sep;142(3):475-494. doi: 10.1007/s00401-021-02325-z. Epub 2021 Jun 14. Acta Neuropathol. 2021. PMID: 34125248 Free PMC article.
-
Development of phospho-specific Rab protein antibodies to monitor in vivo activity of the LRRK2 Parkinson's disease kinase.Biochem J. 2018 Jan 2;475(1):1-22. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20170802. Biochem J. 2018. PMID: 29127256 Free PMC article.
-
Rab10 Phosphorylation is a Prominent Pathological Feature in Alzheimer's Disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;63(1):157-165. doi: 10.3233/JAD-180023. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018. PMID: 29562525 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocerebrosidase 1 and leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 in Parkinson disease and interplay between the two genes.J Neurochem. 2021 Dec;159(5):826-839. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15524. Epub 2021 Oct 16. J Neurochem. 2021. PMID: 34618942 Review.
-
Insights into the cellular consequences of LRRK2-mediated Rab protein phosphorylation.Biochem Soc Trans. 2023 Apr 26;51(2):587-595. doi: 10.1042/BST20201145. Biochem Soc Trans. 2023. PMID: 36929701 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Knockdown of Rab9 Recovers Defective Morphological Differentiation Induced by Chemical ER Stress Inducer or PMD-Associated PLP1 Mutant Protein in FBD-102b Cells.Pathophysiology. 2024 Aug 26;31(3):420-435. doi: 10.3390/pathophysiology31030032. Pathophysiology. 2024. PMID: 39311306 Free PMC article.
-
Protein modification in neurodegenerative diseases.MedComm (2020). 2024 Aug 4;5(8):e674. doi: 10.1002/mco2.674. eCollection 2024 Aug. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39105197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[MiRNA-103-3p promotes neural cell autophagy by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling via targeting rab10 in a rat model of depression].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2024 Jul 20;44(7):1315-1326. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.07.11. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2024. PMID: 39051077 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Role of LRRK2 in axonal transport and Parkinson's disease.Biochem J. 2025 Jun 25;482(13):905-19. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20253133. Biochem J. 2025. PMID: 40570189 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RAB3 phosphorylation by pathogenic LRRK2 impairs trafficking of synaptic vesicle precursors.J Cell Biol. 2024 Jun 3;223(6):e202307092. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202307092. Epub 2024 Mar 21. J Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38512027 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aosaki T, Miura M, Masuda M. Physiological interaction between acetylcholine and dopamine in the striatum. Brain Nerve. 2009;61:373–380. - PubMed
-
- Beccano-Kelly DA, Kuhlmann N, Tatarnikov I, Volta M, Munsie LN, Chou P, Cao LP, Han H, Tapia L, Farrer MJ, Milnerwood AJ. Synaptic function is modulated by LRRK2 and glutamate release is increased in cortical neurons of G2019S LRRK2 knock-in mice. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014;8:301. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00301. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

