Central activation of the fatty acid sensor GPR120 suppresses microglia reactivity and alleviates sickness- and anxiety-like behaviors
- PMID: 38111048
- PMCID: PMC10729532
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-023-02978-5
Central activation of the fatty acid sensor GPR120 suppresses microglia reactivity and alleviates sickness- and anxiety-like behaviors
Abstract
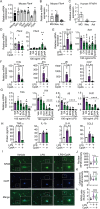
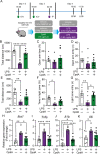
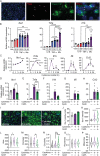
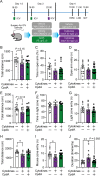
G protein-coupled receptor 120 (GPR120, Ffar4) is a sensor for long-chain fatty acids including omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (n-3 PUFAs) known for beneficial effects on inflammation, metabolism, and mood. GPR120 mediates the anti-inflammatory and insulin-sensitizing effects of n-3 PUFAs in peripheral tissues. The aim of this study was to determine the impact of GPR120 stimulation on microglial reactivity, neuroinflammation and sickness- and anxiety-like behaviors by acute proinflammatory insults. We found GPR120 mRNA to be enriched in both murine and human microglia, and in situ hybridization revealed GPR120 expression in microglia of the nucleus accumbens (NAc) in mice. In a manner similar to or exceeding n-3 PUFAs, GPR120 agonism (Compound A, CpdA) strongly attenuated lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced proinflammatory marker expression in primary mouse microglia, including tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and inhibited nuclear factor-ĸB translocation to the nucleus. Central administration of CpdA to adult mice blunted LPS-induced hypolocomotion and anxiety-like behavior and reduced TNF-α, IL-1β and IBA-1 (microglia marker) mRNA in the NAc, a brain region modulating anxiety and motivation and implicated in neuroinflammation-induced mood deficits. GPR120 agonist pre-treatment attenuated NAc microglia reactivity and alleviated sickness-like behaviors elicited by central injection TNF-α and IL-1β. These findings suggest that microglial GPR120 contributes to neuroimmune regulation and behavioral changes in response to acute infection and elevated brain cytokines. GPR120 may participate in the protective action of n-3 PUFAs at the neural and behavioral level and offers potential as treatment target for neuroinflammatory conditions.
Keywords: Anxiety; Behavioral neuroimmunology; Endotoxemia; Ffar4; Free fatty acid receptor; Locomotion; Neuropharmacology; Nucleus accumbens; Sickness behaviors.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Décarie-Spain L, Sharma S, Hryhorczuk C, Issa-Garcia V, Barker PA, Arbour N, Alquier T, Fulton S. Nucleus accumbens inflammation mediates anxiodepressive behavior and compulsive sucrose seeking elicited by saturated dietary fat. Mol Metab. 2018;10:1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2018.01.018. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

