De novo identification of expressed cancer somatic mutations from single-cell RNA sequencing data
- PMID: 38111063
- PMCID: PMC10726641
- DOI: 10.1186/s13073-023-01269-1
De novo identification of expressed cancer somatic mutations from single-cell RNA sequencing data
Erratum in
-
Correction: Genome Med 15, 115 & Genome Med 16, 3.Genome Med. 2024 May 14;16(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s13073-024-01343-2. Genome Med. 2024. PMID: 38745249 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
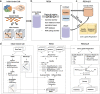
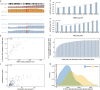
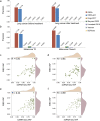
Identifying expressed somatic mutations from single-cell RNA sequencing data de novo is challenging but highly valuable. We propose RESA - Recurrently Expressed SNV Analysis, a computational framework to identify expressed somatic mutations from scRNA-seq data. RESA achieves an average precision of 0.77 on three in silico spike-in datasets. In extensive benchmarking against existing methods using 19 datasets, RESA consistently outperforms them. Furthermore, we applied RESA to analyze intratumor mutational heterogeneity in a melanoma drug resistance dataset. By enabling high precision detection of expressed somatic mutations, RESA substantially enhances the reliability of mutational analysis in scRNA-seq. RESA is available at https://github.com/ShenLab-Genomics/RESA .
Keywords: High precision; Recurrently Expressed SNV Analysis; Single-cell RNA sequencing data; Somatic mutations.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have submitted a patent application for the method. Other than this, the authors declare that they do not have any competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

