Infliximab-induced retrobulbar optic neuritis in a patient with ankylosing spondylitis
- PMID: 38111472
- PMCID: PMC10726561
- DOI: 10.3205/oc000232
Infliximab-induced retrobulbar optic neuritis in a patient with ankylosing spondylitis
Abstract
Objective: To present a case with infliximab-induced retrobulbar optic neuritis.
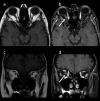
Case description: A 58-year-old woman presented to our clinic with a two-day history of blurred vision in her right eye. She had numerous uveitis attacks previously, and she was on infliximab treatment for ankylosing spondylitis. Her best-corrected visual acuity was counting fingers and 20/25 in the right and left eye, respectively. Optic discs seemed healthy in fundoscopic examination. The right optic nerve showed high signal intensity on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Infliximab treatment was discontinued and systemic steroid therapy was started. After the treatment her best-corrected visual acuity improved to 20/20 in her right eye.
Conclusion: Infliximab is a chimeric human-murine monoclonal antibody used in autoimmune diseases. Optic neuritis is a rare but important side effect of infliximab. Thus, infliximab-induced optic neuritis should be kept in mind for patients receiving infliximab treatment.
Keywords: ankylosing spondylitis; anti-TNF; demyelinating disease; infliximab; optic neuritis.
Copyright © 2023 Dündar et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Song M, Li F, Xie X, Chen J, Tang M, Tian J, Du J, Ge Y, Li S, Xu S. 英夫利西单抗治疗类风湿关节炎的短期疗效及其与血药浓度和抗药物抗体的关联. [Association of short-term efficacy for infliximab in rheumatoid arthritis with plasma concentration and anti-drug antibody]. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2018 Sep;43(9):982–986. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2018.09.008. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials