UV-Vis detection of E. coli 0157:H7 using Vitis vinifera and Musa paradaisica modified Au-NPs
- PMID: 38111791
- PMCID: PMC10727931
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mex.2023.102522
UV-Vis detection of E. coli 0157:H7 using Vitis vinifera and Musa paradaisica modified Au-NPs
Abstract
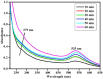
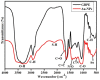
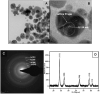
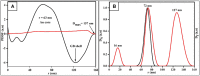
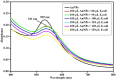
Herein, we demonstrate the simple one-pot novel green synthesis of gold nanoparticles (Au-NPs) functionalised with a combination of banana peel (Musa paradaisica) and grape (Vitis vinifera) fruit extracts. The reaction mixture of aqueous gold chloride, banana peel and grape extracts revealed a purple colour after a reaction time of one hour, an indication of the presence and the successful synthesis of gold nanoparticles. The optical and structural properties of the green synthesized nanoparticles were analysed using Ultraviolet-Visible spectroscopy (UV-Vis) and Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) while their surface morphology was determined using X-Ray Diffraction (XRD), High-Resolution Transmission Microscopy (HRTEM) and Small Angle X-Ray (SAX). Furthermore, a quick and simple surface plasmon resonance (SPR) study in the form of an optical sensor for the detection of Escherichia coli 0157:H7 strain was also achieved using UV-Vis. The obtained limit of detection (LOD) value for SPR for the GBPE|Au-NPs|GCE-based system was found to be 1 × 102 CFU/mL, a value well in the range for detection in seawater.•Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles (Au-NPs) was functionalised using banana peel (Musa paradaisica) and grape (Vitis vinifera) fruit extracts as capping and stabilizing agents.•Structural characterization of the Au-NPs was achieved using Ultraviolet-Visible spectroscopy (UV-Vis) and Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) while their surface morphology was determined using X-Ray Diffraction (XRD), High-Resolution Transmission Microscopy (HRTEM) and Small Angle X-Ray (SAX).•The green synthesized Au-NPs were used to detect Escherichia coli 0157:H7 (E. coli 0157:H7) strain using Ultraviolet-Visible spectroscopy (UV-Vis) where the surface plasmon resonance (SPR) was studied.
Keywords: Banana peel; E. coli 0157:H7; Fruit extract; Gold nanoparticles; Grapes; Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles; Musa paradaisica; Vitis vinifera.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could appear to influence the research study reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Ismail H., Khalil M.M.H., Al Seif F.A., El-Maghdoub F. Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles using extract of grape (Vitis vinifera) leaves and seeds. Prog. Nanotechnol. Nanomater. 2014;3:1–12.
-
- Mukundan S.D., Mohankumar R., Vasanthakumar R. Comparative study of synthesized silver and gold nanoparticles using leaves extract of Bauhinia tomentosa Linn and their anticancer efficacy. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2017;40:335–344. doi: 10.1007/s12034-017-1376-2. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

