C-reactive protein levels, the prognostic nutritional index, and the lactate dehydrogenase-to-lymphocyte ratio are important prognostic factors in primary central nervous system lymphoma: a single-center study of 223 patients
- PMID: 38112846
- PMCID: PMC10730673
- DOI: 10.1007/s10143-023-02248-1
C-reactive protein levels, the prognostic nutritional index, and the lactate dehydrogenase-to-lymphocyte ratio are important prognostic factors in primary central nervous system lymphoma: a single-center study of 223 patients
Abstract
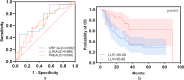
Primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL) is a rare and highly aggressive type of extranodal non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), and the prognosis is poor. Currently, the most used prognostic models are the Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) and International Extranodal Lymphoma Study Group (IELSG) scores; however, their predictive effects are changing with increasing incidence and changing treatment regimens. A growing body of evidence has demonstrated that inflammatory and nutritional markers are factors that can determine tumor prognosis. Therefore, the aim of this study was to identify and validate novel prognostic factors for PCNSL. Clinical information was collected from 223 patients with PCNSL. Patients younger than 18 years of age were excluded. Progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were used as endpoints, and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analyses were conducted to determine the cutoff values for the inflammatory indicators. Correlations between variables and PFS or OS were assessed using univariate and multivariate analyses, and positive indicators were selected for survival analysis. A prognostic nutritional index (PNI) < 49.38 was associated with worse PFS (p = 0.003), and outcomes significantly differed between patients with a PNI ≥ 49.38 and < 49.38 (p < 0.001). Age < 60 years (p < 0.001) and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels < 3.14 (p = 0.001) were associated with better OS. In elderly patients (≥ 60 years), a lactate dehydrogenase-to-lymphocyte ratio (LLR) < 95.69 (p = 0.021) was associated with better OS, and the outcome significantly differed between patients with an LLR ≥ 95.69 and LLR < 95.69 (p = 0.015). The PNI and CRP levels are prognostic factors for PCNSL, and CRP was the first time shown to be a prognosis factor of PCNSL. In elderly patients with PCNSL, the LLR can predict prognosis.
Keywords: C-reactive protein; Elderly patients; Lactate dehydrogenase-to-lymphocyte ratio; Primary central nervous system lymphoma; Prognostic factor; Prognostic nutritional index.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Letter to editor: C‑reactive protein levels, the prognostic nutritional index, and the lactate dehydrogenase‑to‑lymphocyte ratio are important prognostic factors in primary central nervous system lymphoma: a single‑center study of 223 patients.Neurosurg Rev. 2024 Apr 11;47(1):146. doi: 10.1007/s10143-024-02387-z. Neurosurg Rev. 2024. PMID: 38600419
-
A Novel Prognostic Marker for Primary CNS Lymphoma: Lactate Dehydrogenase-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Improves Stratification of Patients Within the Low and Intermediate MSKCC Risk Groups.Front Oncol. 2021 Aug 3;11:696147. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.696147. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34422649 Free PMC article.
-
A novel prognostic model based on pretreatment serum albumin and ECOG PS for primary CNS lymphoma: an international, multi-center study.J Neurooncol. 2023 Jun;163(2):301-311. doi: 10.1007/s11060-023-04337-z. Epub 2023 May 26. J Neurooncol. 2023. PMID: 37231231
-
Pretreatment Hemoglobin as an Independent Prognostic Factor in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphomas.Oncologist. 2019 Sep;24(9):e898-e904. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0629. Epub 2019 Mar 13. Oncologist. 2019. PMID: 30867243 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of primary central nervous system lymphoma in the elderly population (Review).Int J Oncol. 2021 Mar;58(3):371-387. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2021.5180. Epub 2021 Feb 1. Int J Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33650642 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic and clinicopathological role of prognostic nutritional index (PNI) in endometrial cancer: A meta-analysis.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 25;10(15):e35211. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35211. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39157381 Free PMC article.
-
Comment on, "Creactive protein levels, the prognostic nutritional index, and the lactate dehydrogenasetolymphocyte ratio are important prognostic factors in primary central nervous system lymphoma: a singlecenter study of 223 patients".Neurosurg Rev. 2024 Sep 27;47(1):697. doi: 10.1007/s10143-024-02924-w. Neurosurg Rev. 2024. Retraction in: Neurosurg Rev. 2025 Jan 28;48(1):98. doi: 10.1007/s10143-025-03252-3. PMID: 39327337 Retracted.
-
A Nomogram for Predicting Overall Survival in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma: A Retrospective Study.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Feb 10;18:2091-2103. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S498121. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 39959640 Free PMC article.
-
Letter to editor: C‑reactive protein levels, the prognostic nutritional index, and the lactate dehydrogenase‑to‑lymphocyte ratio are important prognostic factors in primary central nervous system lymphoma: a single‑center study of 223 patients.Neurosurg Rev. 2024 Apr 11;47(1):146. doi: 10.1007/s10143-024-02387-z. Neurosurg Rev. 2024. PMID: 38600419
References
-
- WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board (2021) World Health Organization Classification of Tumours of the Central Nervous System. 5th ed. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer
-
- Haldorsen IS, Krossnes BK, Aarseth JH, Scheie D, Johannesen TB, Mella O, Espeland A (2007) Increasing incidence and continued dismal outcome of primary central nervous system lymphoma in Norway 1989–2003: time trends in a 15-year national survey. Cancer 110:1803–1814. 10.1002/cncr.22989 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

