Developing a Tool for Differentiation Between Bacterial and Viral Respiratory Infections Using Myxovirus Resistance Protein A and C-Reactive Protein
- PMID: 38112973
- PMCID: PMC10828347
- DOI: 10.1007/s40121-023-00901-2
Developing a Tool for Differentiation Between Bacterial and Viral Respiratory Infections Using Myxovirus Resistance Protein A and C-Reactive Protein
Abstract
Introduction: The aim was to assess the performance of a blood assay combining measurements of MxA (myxovirus resistance protein A) and CRP (C-reactive protein) to differentiate viral from bacterial respiratory infections.
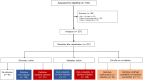
Methods: In a prospective study, MxA and CRP were measured in the blood by the AFIAS panel in adults admitted with respiratory infection. Patients were split into discovery and validation cohorts. Final diagnosis was adjudicated by a panel of experts. Microbiology-confirmed cases comprised the discovery cohort, and infections adjudicated as highly probable viral or bacterial comprised the validation cohort.
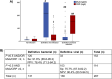
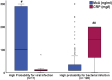
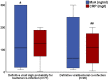
Results: A total of 537 patients were analyzed: 136 patients were adjudicated with definitive viral infections and 131 patients with definitive bacterial infections. Using logistic regression analysis, an equation was developed to calculate the probability for bacterial infection using the absolute value of MxA and CRP. Calculated probability ≥ 0.5 and/or MxA to CRP ratio less than 2 applied as the diagnostic rule for bacterial infections. This rule provided 91.6% sensitivity and 90.4% negative predictive value for the diagnosis of bacterial infections. This diagnostic sensitivity was confirmed in the validation cohort. A MxA/CRP ratio less than 0.15 was associated with unfavorable outcome.
Conclusion: The calculation of the probability for bacterial infection using MxA and CRP may efficiently discriminate between viral and bacterial respiratory infections.
Keywords: Bacterial infection; CRP; Diagnosis; MxA; Viral infection.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Garyphalia. Poulakou has received honoraria and/or consulting fees by Astra-Zeneca, Gilead, GSK, Menarini, MSD, Norma, Pfizer and SOBI and research grants by the University of Minnesota/University College London, the Hellenic Institute for the Study of Sepsis, Bausch, Roche, Xenothera, FabNTech and Pfizer. Ilias C. Papanikolaou has received honoraria or served as PI for studies from Boehringer-Ingelheim, GlaxoSmithKline and AstraZeneca. Haralampos. Milionis reports receiving honoraria, consulting fees and non-financial support from healthcare companies, including Amgen, Angelini, Bayer, Mylan, MSD, Pfizer, and Servier. George N Dalekos is an advisor or lecturer for Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi and Sobi, and received research grants from Gilead and has served as PI in studies for Gilead, Novo Nordisk, Genkyotex, Regulus Therapeutics Inc, Tiziana Life Sciences, Bayer, Astellas, Pfizer, Amyndas Pharmaceuticals, CymaBay Therapeutics Inc., Sobi and Intercept Pharmaceuticals. Evangelos. J. Giamarellos-Bourboulis has received honoraria from Abbott Products Operations, bioMérieux, Brahms GmbH, GSK, InflaRx GmbH, Sobi and Xbiotech Inc; independent educational grants from Abbott Products Operations, bioMérieux Inc, InflaRx GmbH, Johnson & Johnson, MSD, Sobi and Xbiotech Inc.; and funding from the Horizon2020 Marie Skłodowska-Curie International Training Network “the European Sepsis Academy” (granted to the National and Kapodistrian University of Athens), the Horizon 2020 European Grants ImmunoSep and RISCinCOVID and the Horizon Health grant EPIC-CROWN-2 (granted to the Hellenic Institute for the Study of Sepsis). Konstantina Iliopoulou, Panagiotis Koufargyris, Sarantia Doulou, Elisavet Tasouli, Sokratis Katopodis, Stavroula-Porphyria Chachali, Georgios Schinas, Charalambos Karachalios, Myrto Astriti, Parakevi Katsaounou, George Chrysos, Theodors Seferlis, Effrosyni Dimopoulou, Myrto Kollia, Styliani Gerakari, Vasiliki Tzavara, and Theano Kontopoulou have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Recent updates of interferon-derived myxovirus resistance protein A as a biomarker for acute viral infection.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Dec 23;29(1):612. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-02221-8. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39710743 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of myxovirus resistance protein A in the etiological diagnosis of infections in adults.World J Emerg Med. 2025;16(1):35-42. doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2025.011. World J Emerg Med. 2025. PMID: 39906110 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical application of Myxovirus resistance protein A as a diagnostic biomarker to differentiate viral and bacterial respiratory infections in pediatric patients.Front Immunol. 2025 Feb 19;16:1540675. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1540675. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40046054 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of a combined MxA and CRP point-of-care immunoassay to identify viral and/or bacterial immune response in patients with acute febrile respiratory infection.Eur Clin Respir J. 2015 Dec 10;2:28245. doi: 10.3402/ecrj.v2.28245. eCollection 2015. Eur Clin Respir J. 2015. PMID: 26672961 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon-Inducible Myxovirus Resistance Proteins: Potential Biomarkers for Differentiating Viral from Bacterial Infections.Clin Chem. 2019 Jun;65(6):739-750. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2018.292391. Epub 2018 Dec 28. Clin Chem. 2019. PMID: 30593466 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recent updates of interferon-derived myxovirus resistance protein A as a biomarker for acute viral infection.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Dec 23;29(1):612. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-02221-8. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39710743 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of myxovirus resistance protein A in the etiological diagnosis of infections in adults.World J Emerg Med. 2025;16(1):35-42. doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2025.011. World J Emerg Med. 2025. PMID: 39906110 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers to guide sepsis management.Ann Intensive Care. 2025 Jul 21;15(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s13613-025-01524-1. Ann Intensive Care. 2025. PMID: 40685448 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

