Diagnostic accuracy of endocytoscopy via artificial intelligence in colorectal lesions: A systematic review and meta‑analysis
- PMID: 38113199
- PMCID: PMC10729963
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0294930
Diagnostic accuracy of endocytoscopy via artificial intelligence in colorectal lesions: A systematic review and meta‑analysis
Abstract
Background: Endocytoscopy (EC) is a nuclei and micro-vessels visualization in real-time and can facilitate "optical biopsy" and "virtual histology" of colorectal lesions. This study aimed to investigate the significance of employing artificial intelligence (AI) in the field of endoscopy, specifically in diagnosing colorectal lesions. The research was conducted under the supervision of experienced professionals and trainees.
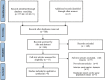
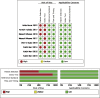
Methods: EMBASE, PubMed, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) database, and other potential databases were surveyed for articles related to the EC with AI published before September 2023. RevMan (5.40), Stata (14.0), and R software (4.1.0) were used for statistical assessment. Studies that measured the accuracy of EC using AI for colorectal lesions were included. Two authors independently assessed the selected studies and their extracted data. This included information such as the country, literature, total study population, study design, characteristics of the fundamental study and control groups, sensitivity, number of samples, assay methodology, specificity, true positives or negatives, and false positives or negatives. The diagnostic accuracy of EC by AI was determined by a bivariate random-effects model, avoiding a high heterogeneity effect. The ANOVA model was employed to determine the more effective approach.
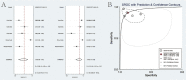
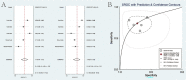
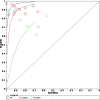
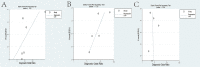
Results: A total of 223 studies were reviewed; 8 articles were selected that included 2984 patients (4241 lesions) for systematic review and meta-analysis. AI assessed 4069 lesions; experts diagnosed 3165 and 5014 by trainees. AI demonstrated high accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity levels in detecting colorectal lesions, with values of 0.93 (95% CI: 0.90, 0.95) and 0.94 (95% CI: 0.73, 0.99). Expert diagnosis was 0.90 (95% CI: 0.85, 0.94), 0.87 (95% CI: 0.78, 0.93), and trainee diagnosis was 0.74 (95% CI: 0.67, 0.79), 0.72 (95% CI: 0.62, 0.80). With the EC by AI, the AUC from SROC was 0.95 (95% CI: 0.93, 0.97), therefore classified as excellent category, expert showed 0.95 (95% CI: 0.93, 0.97), and the trainee had 0.79 (95% CI: 0.75, 0.82). The superior index from the ANOVA model was 4.00 (1.15,5.00), 2.00 (1.15,5.00), and 0.20 (0.20,0.20), respectively. The examiners conducted meta-regression and subgroup analyses to evaluate the presence of heterogeneity. The findings of these investigations suggest that the utilization of NBI technology was correlated with variability in sensitivity and specificity. There was a lack of solid evidence indicating the presence of publishing bias.
Conclusions: The present findings indicate that using AI in EC can potentially enhance the efficiency of diagnosing colorectal abnormalities. As a valuable instrument, it can enhance prognostic outcomes in ordinary EC procedures, exhibiting superior diagnostic accuracy compared to trainee-level endoscopists and demonstrating comparability to expert endoscopists. The research is subject to certain constraints, namely a limited number of clinical investigations and variations in the methodologies used for identification. Consequently, it is imperative to conduct comprehensive and extensive research to enhance the precision of diagnostic procedures.
Copyright: © 2023 Zhang et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Accuracy of artificial intelligence on histology prediction and detection of colorectal polyps: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Gastrointest Endosc. 2020 Jul;92(1):11-22.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2020.02.033. Epub 2020 Feb 29. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020. PMID: 32119938
-
Artificial intelligence-assisted capsule endoscopy for detecting lesions in Crohn's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Artif Intell. 2025 Apr 1;8:1531362. doi: 10.3389/frai.2025.1531362. eCollection 2025. Front Artif Intell. 2025. PMID: 40235858 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial Intelligence-assisted System Improves Endoscopic Identification of Colorectal Neoplasms.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Jul;18(8):1874-1881.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.09.009. Epub 2019 Sep 13. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 31525512
-
Imaging modalities to inform the detection and diagnosis of early caries.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 15;3(3):CD014545. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014545. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33720395 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Performance of Artificial Intelligence-Based Models for the Detection of Early Esophageal Cancers in Barret's Esophagus: A Meta-Analysis of Patient-Based Studies.Cureus. 2021 Jun 4;13(6):e15447. doi: 10.7759/cureus.15447. eCollection 2021 Jun. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34258114 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Emerging Technologies in Endoscopy for Gastrointestinal Neoplasms: A Comprehensive Overview.Cureus. 2024 Jun 23;16(6):e62946. doi: 10.7759/cureus.62946. eCollection 2024 Jun. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39044885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Texture and Color Enhancement Imaging-Assisted Endocytoscopy Improves Characterization of Gastric Precancerous Conditions: A Set of Interesting Comparative Images.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Jul 31;15(15):1925. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15151925. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40804890 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Intelligence and Early Detection of Breast, Lung, and Colon Cancer: A Narrative Review.Cureus. 2025 Feb 18;17(2):e79199. doi: 10.7759/cureus.79199. eCollection 2025 Feb. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40125138 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- KUDO T, SUZUKI K, MORI Y, et al.. Endocytoscopy for the differential diagnosis of colorectal low-grade adenoma: a novel possibility for the "resect and discard" strategy [J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2020, 91(3): 676–83. - PubMed
-
- REUMKENS A, RONDAGH E J, BAKKER C M, et al.. Post-Colonoscopy Complications: A Systematic Review, Time Trends, and Meta-Analysis of Population-Based Studies [J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2016, 111(8): 1092–101. - PubMed
-
- BISSCHOPS R, EAST J E, HASSAN C, et al.. Advanced imaging for detection and differentiation of colorectal neoplasia: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline—Update 2019 [J]. Endoscopy, 2019, 51(12): 1155–79. - PubMed
-
- ARNOLD M, SIERRA M S, LAVERSANNE M, et al.. Global patterns and trends in colorectal cancer incidence and mortality [J]. Gut, 2017, 66(4): 683–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

