Acidic Osteoid Templates the Plywood Structure of Bone Tissue
- PMID: 38115757
- PMCID: PMC10916609
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202304454
Acidic Osteoid Templates the Plywood Structure of Bone Tissue
Abstract
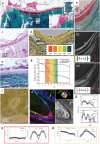
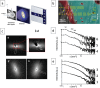
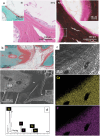
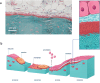
Bone is created by osteoblasts that secrete osteoid after which an ordered texture emerges, followed by mineralization. Plywood geometries are a hallmark of many trabecular and cortical bones, yet the origin of this texturing in vivo has never been shown. Nevertheless, extensive in vitro work revealed how plywood textures of fibrils can emerge from acidic molecular cholesteric collagen mesophases. This study demonstrates in sheep, which is the preferred model for skeletal orthopaedic research, that the deeper non-fibrillar osteoid is organized in a liquid-crystal cholesteric geometry. This basophilic domain, rich in acidic glycosaminoglycans, exhibits low pH which presumably fosters mesoscale collagen molecule ordering in vivo. The results suggest that the collagen fibril motif of twisted plywood matures slowly through self-assembly thermodynamically driven processes as proposed by the Bouligand theory of biological analogues of liquid crystals. Understanding the steps of collagen patterning in osteoid-maturation processes may shed new light on bone pathologies that emerge from collagen physico-chemical maturation imbalances.
Keywords: acidity; biomineralization; bone; collagen; liquid-crystal; osteoid; plywood.
© 2023 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Twisted plywood architecture of collagen fibrils in human compact bone osteons.Calcif Tissue Int. 1988 Mar;42(3):167-80. doi: 10.1007/BF02556330. Calcif Tissue Int. 1988. PMID: 3130165
-
Liquid crystalline assemblies of collagen in bone and in vitro systems.J Biomech. 2003 Oct;36(10):1571-9. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9290(03)00134-9. J Biomech. 2003. PMID: 14499304 Review.
-
New method for Raman investigation of the orientation of collagen fibrils and crystallites in the Haversian system of bone.Appl Spectrosc. 2010 Jul;64(7):775-80. doi: 10.1366/000370210791666255. Appl Spectrosc. 2010. PMID: 20615291
-
Structure and formation of the twisted plywood pattern of collagen fibrils in rat lamellar bone.J Electron Microsc (Tokyo). 2012 Apr;61(2):113-21. doi: 10.1093/jmicro/dfs033. Epub 2012 Feb 22. J Electron Microsc (Tokyo). 2012. PMID: 22362877
-
Alternating lamellar structure in human cellular cementum and rat compact bone: Its structure and formation.J Oral Biosci. 2019 Jun;61(2):105-114. doi: 10.1016/j.job.2019.03.006. Epub 2019 May 15. J Oral Biosci. 2019. PMID: 31109862 Review.
References
-
- Neville A. C., Biology of Fibrous Composites: Development Beyond the Cell Membrane, Cambridge University Press, 1993.
-
- Parfitt A. M., J. Cell. Biochem. 1994, 55, 273. - PubMed
-
- Mckee M. D., Nanci A., Microsc. Res. Tech. 1996, 33, 141. - PubMed
-
- Ingram R. T., Clarke B. L., Fisher L. W., Fitzpatrick L. A., J. Bone Miner. Res. 1993, 8, 1019. - PubMed
-
- Alford A. I., Kozloff K. M., Hankenson K. D., Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2015, 65, 20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
