Biology of endophilin and it's role in disease
- PMID: 38116012
- PMCID: PMC10728279
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1297506
Biology of endophilin and it's role in disease
Abstract
Endophilin is an evolutionarily conserved family of protein that involves in a range of intracellular membrane dynamics. This family consists of five isoforms, which are distributed in various tissues. Recent studies have shown that Endophilin regulates diseases pathogenesis, including neurodegenerative diseases, tumors, cardiovascular diseases, and autoimmune diseases. In vivo, it regulates different biological functions such as vesicle endocytosis, mitochondrial morphological changes, apoptosis and autophagosome formation. Functional studies confirmed the role of Endophilin in development and progression of these diseases. In this study, we have comprehensively discussed the complex function of Endophilin and how the family contributes to diseases development. It is hoped that this study will provide new ideas for targeting Endophilin in diseases.
Keywords: autophagy; diseases; endocytosis; endophilin; function.
Copyright © 2023 Yang, Huang and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
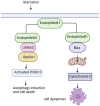
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

