NLRP3/IL-1β induced myeloid-derived suppressor cells recruitment and PD-L1 upregulation promotes oxaliplatin resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 38116060
- PMCID: PMC10728756
- DOI: 10.1002/mco2.447
NLRP3/IL-1β induced myeloid-derived suppressor cells recruitment and PD-L1 upregulation promotes oxaliplatin resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
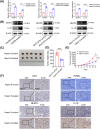
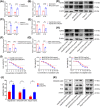
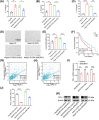
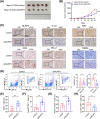
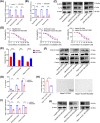
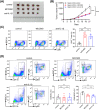
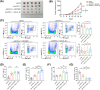
Oxaliplatin is commonly used as the first-line chemotherapeutic agent for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Unfortunately, the acquired resistance, limits the effectiveness of oxaliplatin and the underlying mechanisms remain unknown. Therefore, we explored the role of NOD-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3)/IL-1β in mediating oxaliplatin resistance in HCC. We observed that NLRP3/IL-1β expression was much higher in oxaliplatin-resistant HCC cells. To further understand its impact on drug resistance, we knocked down NLRP3 and observed that it sensitized HCC cells to the growth-inhibitory effects of oxaliplatin and induced cell apoptosis. NLRP3/IL-1β overexpressing tumor cells also attracted polymorphonuclear myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Using mouse models, we demonstrated that NLRP3/IL-1β inhibition by short hairpin RNA or MCC950 effectively overcame oxaliplatin resistance. Furthermore, NLRP3/IL-1β inhibition resulted in reduced expression of PD-L1. We also found that PD-L1 antibody combined with NLRP3/IL-1β blockade displayed significant antitumor effect in HCC. Overall, our study provides compelling evidence supporting the essential role of NLRP3/IL-1β in conferring resistance to oxaliplatin and reshaping the immunosuppressive microenvironment in HCC. Targeting NLRP3/IL-1β presents a potential therapeutic target for overcoming oxaliplatin resistance and reshaping microenvironment of HCC.
Keywords: NLRP3/IL‐1β; PD‐L1; hepatocellular carcinoma; myeloid‐derived suppressor cells; oxaliplatin resistance.
© 2023 The Authors. MedComm published by Sichuan International Medical Exchange & Promotion Association (SCIMEA) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Couri T, Pillai A. Goals and targets for personalized therapy for HCC. Hepatol Int. 2019;13(2):125‐137. - PubMed
-
- Raoul JL, Forner A, Bolondi L, et al. Updated use of TACE for hepatocellular carcinoma treatment: how and when to use it based on clinical evidence. Cancer Treat Rev. 2019;72:28‐36. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
