CsrA selectively modulates sRNA-mRNA regulator outcomes
- PMID: 38116378
- PMCID: PMC10729762
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1249528
CsrA selectively modulates sRNA-mRNA regulator outcomes
Abstract
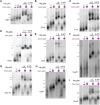
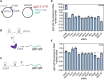
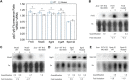
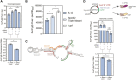
Post-transcriptional regulation, by small RNAs (sRNAs) as well as the global Carbon Storage Regulator A (CsrA) protein, play critical roles in bacterial metabolic control and stress responses. The CsrA protein affects selective sRNA-mRNA networks, in addition to regulating transcription factors and sigma factors, providing additional avenues of cross talk between other stress-response regulators. Here, we expand the known set of sRNA-CsrA interactions and study their regulatory effects. In vitro binding assays confirm novel CsrA interactions with ten sRNAs, many of which are previously recognized as key regulatory nodes. Of those 10 sRNA, we identify that McaS, FnrS, SgrS, MicL, and Spot42 interact directly with CsrA in vivo. We find that the presence of CsrA impacts the downstream regulation of mRNA targets of the respective sRNA. In vivo evidence supports enhanced CsrA McaS-csgD mRNA repression and showcases CsrA-dependent repression of the fucP mRNA via the Spot42 sRNA. We additionally identify SgrS and FnrS as potential new sRNA sponges of CsrA. Overall, our results further support the expanding impact of the Csr system on cellular physiology via CsrA impact on the regulatory roles of these sRNAs.
Keywords: CsrA/RsmA; Posttranscriptional regulation; RNA-protein interactions; sRNA (small RNA); sRNA regulatory network.
Copyright © 2023 Rojano-Nisimura, Simmons, Leistra, Mihailovic, Buchser, Ekdahl, Joseph, Curtis and Contreras.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Andreassen P. R., Pettersen J. S., Szczerba M., Valentin-Hansen P., Møller-Jensen J., Jørgensen M. G. (2018). sRNA-dependent control of curli biosynthesis in Escherichia coli: mcaS directs endonucleolytic cleavage of csgD mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 46 (13), 6746–6760. 10.1093/nar/gky479 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

