Enhancing health resilience in Japan in a changing climate
- PMID: 38116496
- PMCID: PMC10730320
- DOI: 10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100970
Enhancing health resilience in Japan in a changing climate
Abstract
Climate change poses significant threats to human health, propelling Japan to take decisive action through the Climate Change Adaptation Act of 2018. This Act has led to the implementation of climate change adaptation policies across various sectors, including healthcare. In this review, we synthesized existing scientific evidence on the impacts of climate change on health in Japan and outlined the adaptation strategies and measures implemented by the central and local governments. The country has prioritized tackling heat-related illness and mortality and undertaken various adaptation measures to mitigate these risks. However, it faces unique challenges due to its super-aged society. Ensuring effective and coordinated strategies to address the growing uncertainties in vulnerability to climate change and the complex intersectoral impacts of disasters remains a critical issue. To combat the additional health risks by climate change, a comprehensive approach embracing adaptation and mitigation policies in the health sector is crucial. Encouraging intersectoral communication and collaboration will be vital for developing coherent and effective strategies to safeguard public health in the face of climate change.
Keywords: Adaptation measures; Climate change; Health impacts; Heat; Japan.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
KO received the Environment Research and Technology Development Fund of the Environmental Restoration and Conservation Agency. YK was supported by the University of Tokyo Excellent Young Researcher award.
Figures
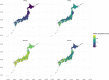
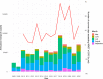

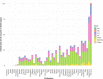
References
-
- Ministry of the Environment, Japan (MOEJ) Assessment report on climate change impacts in Japan. MOEJ. 2020 https://www.env.go.jp/content/000047546.pdf
-
- New M., Reckien D., Viner D., et al. In: Climate change 2022: impacts, adaptation and vulnerability contribution of working group II to the sixth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Pörtner H.-O., Roberts D.C., Tignor M., et al., editors. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA: 2022. Decision-making options for managing risk.
-
- Sharifi A., Pathak M., Joshi C., He B.-J. A systematic review of the health co-benefits of urban climate change adaptation. Sustain Cities Soc. 2021;74
-
- World Bank Group. Japan . 2021. https://climateknowledgeportal.worldbank.org/country/japan
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

