Oral nitrate supplementation improves cardiovascular risk markers in COPD: ON-BC, a randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 38123239
- PMCID: PMC10831142
- DOI: 10.1183/13993003.02353-2022
Oral nitrate supplementation improves cardiovascular risk markers in COPD: ON-BC, a randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Short-term studies suggest that dietary nitrate (NO3 -) supplementation may improve the cardiovascular risk profile, lowering blood pressure (BP) and enhancing endothelial function. It is not clear if these beneficial effects are sustained and whether they apply in people with COPD, who have a worse cardiovascular profile than those without COPD. Nitrate-rich beetroot juice (NR-BRJ) is a convenient dietary source of nitrate.
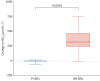
Methods: The ON-BC trial was a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled parallel group study in stable COPD patients with home systolic BP (SBP) measurement ≥130 mmHg. Participants were randomly allocated (1:1) using computer-generated, block randomisation to either 70 mL NR-BRJ (400 mg NO3 -) (n=40) or an otherwise identical nitrate-depleted placebo juice (0 mg NO3 -) (n=41), once daily for 12 weeks. The primary end-point was between-group change in home SBP measurement. Secondary outcomes included change in 6-min walk distance (6MWD) and measures of endothelial function (reactive hyperaemia index (RHI) and augmentation index normalised to a heart rate of 75 beats·min-1 (AIx75)) using an EndoPAT device. Plasma nitrate and platelet function were also measured.
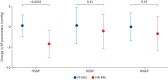
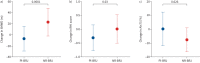
Results: Compared with placebo, active treatment lowered SBP (Hodges-Lehmann treatment effect -4.5 (95% CI -5.9- -3.0) mmHg), and improved 6MWD (30.0 (95% CI 15.7-44.2) m; p<0.001), RHI (0.34 (95% CI 0.03-0.63); p=0.03) and AIx75 (-7.61% (95% CI -14.3- -0.95%); p=0.026).
Conclusions: In people with COPD, prolonged dietary nitrate supplementation in the form of beetroot juice produces a sustained reduction in BP, associated with an improvement in endothelial function and exercise capacity.
Copyright ©The authors 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: T.D. Warner reports grants from British Heart Foundation, outside the submitted work. The remaining authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Comment in
-
"Every beet you take": lowering systolic blood pressure and improving vascular function/exercise capacity via the dietary nitrate-nitrite-NO pathway in patients with COPD.Eur Respir J. 2024 Feb 1;63(2):2302238. doi: 10.1183/13993003.02238-2023. Print 2024 Feb. Eur Respir J. 2024. PMID: 38302179 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Dietary nitrate supplementation to enhance exercise capacity in hypoxic COPD: EDEN-OX, a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised cross-over study.Thorax. 2022 Oct;77(10):968-975. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2021-217147. Epub 2021 Dec 1. Thorax. 2022. PMID: 34853156 Clinical Trial.
-
Oral nitrate supplementation to enhance pulmonary rehabilitation in COPD: ON-EPIC a multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised parallel group study.Thorax. 2020 Jul;75(7):547-555. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2019-214278. Epub 2020 May 6. Thorax. 2020. PMID: 32376732 Clinical Trial.
-
The effect of dietary nitrate supplementation on the oxygen cost of cycling, walking performance and resting blood pressure in individuals with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A double blind placebo controlled, randomised control trial.Nitric Oxide. 2015 Aug 1;48:31-7. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2015.01.002. Epub 2015 Jan 13. Nitric Oxide. 2015. PMID: 25596150 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of dietary nitrate-rich beetroot juice supplementation in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): A systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2021 Apr;42:32-40. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.01.035. Epub 2021 Feb 6. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2021. PMID: 33745600
-
Effectiveness of dietary inorganic nitrate for lowering blood pressure in hypertensive adults: a systematic review.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2019 Mar;17(3):365-389. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2017-003842. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2019. PMID: 30870330
Cited by
-
The Association between Food Groups, Nutraceuticals, and Food Supplements Consumption on Vascular Health Outcomes: A Literature Review.Life (Basel). 2024 Sep 23;14(9):1210. doi: 10.3390/life14091210. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39337992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interventions for the management of concomitant COPD and hypertension: A systematic review.J Multimorb Comorb. 2025 Jun 23;15:26335565251341389. doi: 10.1177/26335565251341389. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. J Multimorb Comorb. 2025. PMID: 40557034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasma nitrate, dietary nitrate, blood pressure, and vascular health biomarkers: a GRADE-Assessed systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Nutr J. 2025 Mar 24;24(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s12937-025-01114-8. Nutr J. 2025. PMID: 40128734 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Beetroot Juice - Effects in Patients with COPD: A Review.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2024 Jul 29;19:1755-1765. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S473397. eCollection 2024. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2024. PMID: 39099609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effects of various nutritional supplements in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a network meta-analysis.BMC Pulm Med. 2025 May 8;25(1):220. doi: 10.1186/s12890-025-03667-0. BMC Pulm Med. 2025. PMID: 40340688 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Chronic respiratory diseases. 2017. www.who.int/health-topics/chronic-respiratory-diseases Date last accessed: 15 April 2017.
-
- Pike D, Lindenmaier TJ, Sin DD, et al. . Imaging evidence of the relationship between atherosclerosis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Imaging Med 2014; 6: 53. doi:10.2217/iim.13.70 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
