Development of a Rapid Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV) Identity Testing Platform through Comprehensive Intact Mass Analysis of Full-Length AAV Capsid Proteins
- PMID: 38123456
- PMCID: PMC10775144
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.3c00513
Development of a Rapid Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV) Identity Testing Platform through Comprehensive Intact Mass Analysis of Full-Length AAV Capsid Proteins
Abstract
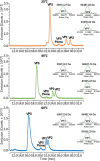
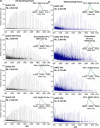
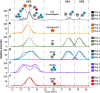
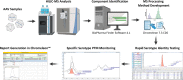
Adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) are commonly used as vectors for the delivery of gene therapy targets. Characterization of AAV capsid proteins (VPs) and their post-translational modifications (PTMs) have become a critical attribute monitored to evaluate product quality. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) analysis of intact AAV VPs provides both quick and reliable serotype identification as well as proteoform information on each VP. Incorporating these analytical strategies into rapid good manufacturing practice (GMP)-compliant workflows containing robust, but simplified, data processing methods is necessary to ensure effective product quality control (QC) during production. Here, we present a GMP-compliant LC-MS workflow for the rapid identification and in-depth characterization of AAVs. Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC) MS with difluoroacetic acid as a mobile phase modifier is utilized to achieve the intact separation and identification of AAV VPs and their potential proteoforms. Peptide mapping is performed to confirm PTMs identified during intact VP analysis and for in-depth PTM characterization. The intact separations platform is then incorporated into a data processing workflow developed using GMP-compliant software capable of rapid AAV serotype identification and, if desired, specific serotype PTM monitoring and characterization. Such a platform provides product QC capabilities that are easily accessible in a regulatory setting.
Keywords: AAV intact viral capsid protein screening; adeno-associated virus; cell and gene therapy; good manufacturing practices; hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography−mass spectrometry; rapid identity testing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): S.G.M. and R.O.S. are employees of Patheon Viral Vector Services. J.B. received funding from Patheon Viral Vector Services to undertake this research. J.S. was employed under the collaborative research engagement between Patheon Viral Vector Services and NIBRT.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

