Layered metal sulfides with MaSbc- framework (M = Sb, In, Sn) as ion exchangers for the removal of Cs(Ⅰ) and Sr(Ⅱ) from radioactive effluents: a review
- PMID: 38124703
- PMCID: PMC10730671
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2023.1292979
Layered metal sulfides with MaSbc- framework (M = Sb, In, Sn) as ion exchangers for the removal of Cs(Ⅰ) and Sr(Ⅱ) from radioactive effluents: a review
Abstract
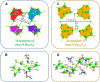
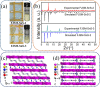
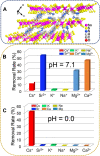
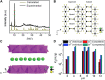
Nuclear power has emerged as a pivotal contributor to the global electricity supply owing to its high efficiency and low-carbon characteristics. However, the rapid expansion of the nuclear industry has resulted in the production of a significant amount of hazardous effluents that contain various radionuclides, such as 137Cs and 90Sr. Effectively removing 137Cs and 90Sr from radioactive effluents prior to discharge is a critical challenge. Layered metal sulfides exhibit significant potential as ion exchangers for the efficient uptake of Cs+ and Sr2+ from aqueous solutions owing to their open and exchangeable frameworks and the distinctive properties of their soft S2- ligands. This review provides a detailed account of layered metal sulfides with MaSb c- frameworks (M = Sb, In, Sn), including their synthesis methods, structural characteristics, and Cs+ and Sr2+ removal efficiencies. Furthermore, we highlight the advantages of layered metal sulfides, such as their relatively high ion exchange capacities, broad active pH ranges, and structural stability against acid and radiation, through a comparative evaluation with other conventional ion exchangers. Finally, we discuss the challenges regarding the practical application of layered metal sulfides in radionuclide scavenging.
Keywords: cesium; ion exchange; layered metal sulfides; radioactive effluents; strontium.
Copyright © 2023 Zhao, Wang, Wu, Wang, Ma and Shih.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Layered Thiostannates with Distinct Arrangements of Mixed Cations for the Selective Capture of Cs+, Sr2+, and Eu3+ Ions.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021 Mar 3;13(8):10191-10201. doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c22690. Epub 2021 Feb 17. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021. PMID: 33595279
-
Highly Efficient Uptake of Cs+ by Robust Layered Metal-Organic Frameworks with a Distinctive Ion Exchange Mechanism.JACS Au. 2022 Jan 20;2(2):492-501. doi: 10.1021/jacsau.1c00533. eCollection 2022 Feb 28. JACS Au. 2022. PMID: 35252998 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient Removal of Cs+ and Sr2+ Ions by Granulous (Me2NH2)4/3(Me3NH)2/3Sn3S7·1.25H2O/Polyacrylonitrile Composite.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021 Mar 24;13(11):13434-13442. doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c01983. Epub 2021 Mar 11. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021. PMID: 33705090
-
Advances in the Efficient Removal of the Key Radioactive Nuclide 90Sr Using Crystalline Ion-Exchange Materials: A Review.Chem Asian J. 2025 Apr 3;20(7):e202401320. doi: 10.1002/asia.202401320. Epub 2025 Feb 20. Chem Asian J. 2025. PMID: 39945673 Review.
-
Recent progress in high-performance environmental impacts of the removal of radionuclides from wastewater based on metal-organic frameworks: a review.RSC Adv. 2023 Aug 23;13(36):25182-25208. doi: 10.1039/d3ra04177h. eCollection 2023 Aug 21. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 37622006 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alby D., Charnay C., Heran M., Prelot B., Zajac J. (2018). Recent developments in nanostructured inorganic materials for sorption of cesium and strontium: synthesis and shaping, sorption capacity, mechanisms, and selectivity—a review. J. Hazard. Mater. 344, 511–530. 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.10.047 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Amesh P., Suneesh A. S., Venkatesan K. A., Uma Maheswari R., Vijayalakshmi S. (2020). Preparation and ion exchange studies of cesium and strontium on sodium iron titanate. Sep. Purif. Technol. 238, 116393. 10.1016/j.seppur.2019.116393 - DOI
-
- Awual M. R. (2016). Ring size dependent crown ether based mesoporous adsorbent for high cesium adsorption from wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 303, 539–546. 10.1016/j.cej.2016.06.040 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

