Effect of beinaglutide combined with metformin versus aspart 30 with metformin on metabolic profiles and antidrug antibodies in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 38125788
- PMCID: PMC10731293
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1267503
Effect of beinaglutide combined with metformin versus aspart 30 with metformin on metabolic profiles and antidrug antibodies in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Objective: This prospective study aimed to evaluate the effect of beinaglutide combined with metformin versus aspart 30 with metformin on metabolic profiles and antidrug antibodies (ADAs) in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D).
Methods: A total of 134 eligible participants were randomly assigned to the test group and the control group. Patients in the test group were treated with beinaglutide and metformin, whereas patients in the control group were randomly treated with aspart 30 and metformin, with a follow-up period of 6 months. The metabolic profiles and ADAs over 6 months were evaluated.
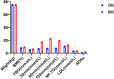
Results: After 6 months, 101 (75.37%) patients completed the study. Compared with the control group, the beinaglutide group had significant reductions in 2-h postprandial blood glucose (2hBG) and low blood glucose index (LBGI). Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) decreased in both groups relative to baseline. In the test group, one had treatment-emergent beinaglutide ADAs. Significant reductions in triglycerides (TG), non-fasting TG, weight, waist circumference (WC), and body mass index (BMI) were observed. The values of insulin sensitivity index (HOMA-IR) were decreased to a statistically higher degree with beinaglutide treatment.
Conclusion: Beinaglutide reduces metabolic dysfunction, LBGI, and weight in patients of T2D with a low risk of ADAs. Beinaglutide may offer the potential for a disease-modifying intervention in cardiovascular disease (CVD).
Clinical trial registration: www.chictr.org.cn, identifier ChiCTR2200061003.
Keywords: anti-drug antibodies; beinaglutide; cardiovascular disease; non-fasting triglyceride; type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2023 Han, Lu, Ye, Jin, Xu, Wang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer PY declared a shared affiliation with the authors to the handling editor at the time of review.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous