Coronary Artery Fistula: A Diagnostic Dilemma
- PMID: 38125927
- PMCID: PMC10731518
- DOI: 10.15420/icr.2022.34
Coronary Artery Fistula: A Diagnostic Dilemma
Abstract
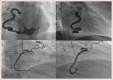
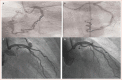
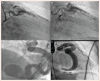
Coronary artery fistula (CAF), although one of the rare coronary anomalies, is becoming increasingly more detectable in the recent years due to advancements in cardiac diagnostic imaging. Its long-term prognostic implications and importance for the cardiovascular system remain a dilemma for cardiologists and patients. Based on a variety of haemodynamic symptoms and complications, cardiologists must be aware of the characteristics of CAF and the diagnostic importance of multi-slice CT in evaluation, pre-procedural management and follow-up. Both surgical and percutaneous options are available for symptomatic patients or those with complications, while management of asymptomatic CAF remains a viable alternative.
Keywords: CT coronary angiography; CTCA; Coronary artery fistula; coronary angiography.
Copyright © The Author(s), 2023. Published by Radcliffe Group Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Stout KK, Daniels CJ, Aboulhosn JA et al. 2018 AHA/ACC Guideline for the management of adults with congenital heart disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2019;139:e698–e800. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000603. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Krause W. On the origin of an accessory coronary artery from the pulmonary artery. Z Ratl Med. 1865;24:225–7. [in German]
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources