Re-evaluation of erythritol (E 968) as a food additive
- PMID: 38125972
- PMCID: PMC10731997
- DOI: 10.2903/j.efsa.2023.8430
Re-evaluation of erythritol (E 968) as a food additive
Abstract
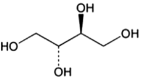
This opinion addresses the re-evaluation of erythritol (E 968) as food additive and an application for its exemption from the laxative warning label requirement as established under Regulation (EU) No 1169/2011. Erythritol is a polyol obtained by fermentation with Moniliella pollinis BC or Moniliella megachiliensis KW3-6, followed by purifications and drying. Erythritol is readily and dose-dependently absorbed in humans and can be metabolised to erythronate to a small extent. Erythritol is then excreted unchanged in the urine. It does not raise concerns regarding genotoxicity. The dataset evaluated consisted of human interventional studies. The Panel considered that erythritol has the potential to cause diarrhoea in humans, which was considered adverse because its potential association with electrolyte and water imbalance. The lower bound of the range of no observed adverse effect levels (NOAELs) for diarrhoea of 0.5 g/kg body weight (bw) was identified as reference point. The Panel considered appropriate to set a numerical acceptable daily intake (ADI) at the level of the reference point. An ADI of 0.5 g/kg bw per day was considered by the Panel to be protective for the immediate laxative effect as well as potential chronic effects, secondary to diarrhoea. The highest mean and 95th percentile chronic exposure was in children (742 mg/kg bw per day) and adolescents (1532 mg/kg bw per day). Acute exposure was maximally 3531 mg/kg bw per meal for children at the 99th percentile. Overall, the Panel considered both dietary exposure assessments an overestimation. The Panel concluded that the exposure estimates for both acute and chronic dietary exposure to erythritol (E 968) were above the ADI, indicating that individuals with high intake may be at risk of experiencing adverse effects after single and repeated exposure. Concerning the new application, the Panel concluded that the available data do not support the proposal for exemption.
Keywords: E 968; diarrhoea; erythritol; food additive; laxative; sweeteners.
© 2023 European Food Safety Authority. EFSA Journal published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH on behalf of European Food Safety Authority.
Conflict of interest statement
If you wish to access the declaration of interests of any expert contributing to an EFSA scientific assessment, please contact interestmanagement@efsa.europa.eu.
Figures
References
-
- Agriculture and Environment Research Unit, University of Hertfordshire , Lewis, K. A. , & Tzilivakis, J. (2021). Review and synthesis of data on the potential environmental impact of artificial sweeteners. EFSA Supporting Publication 18(10), EN‐6918. 10.2903/sp.efsa.2021.EN-6918 - DOI
-
- Bär, A. (1985). Safety assessment of polyol sweeteners – Some aspects of toxicity. Food Chemistry, 16(3–4), 231–241. 10.1016/0308-8146(85)90117-7 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources