Mineralocorticoid receptor overactivation: targeting systemic impact with non-steroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists
- PMID: 38127122
- PMCID: PMC10789668
- DOI: 10.1007/s00125-023-06031-1
Mineralocorticoid receptor overactivation: targeting systemic impact with non-steroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists
Abstract
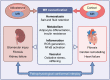
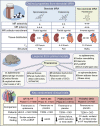
The overactivation of the mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) promotes pathophysiological processes related to multiple physiological systems, including the heart, vasculature, adipose tissue and kidneys. The inhibition of the MR with classical MR antagonists (MRA) has successfully improved outcomes most evidently in heart failure. However, real and perceived risk of side effects and limited tolerability associated with classical MRA have represented barriers to implementing MRA in settings where they have been already proven efficacious (heart failure with reduced ejection fraction) and studying their potential role in settings where they might be beneficial but where risk of safety events is perceived to be higher (renal disease). Novel non-steroidal MRA have distinct properties that might translate into favourable clinical effects and better safety profiles as compared with MRA currently used in clinical practice. Randomised trials have shown benefits of non-steroidal MRA in a range of clinical contexts, including diabetic kidney disease, hypertension and heart failure. This review provides an overview of the literature on the systemic impact of MR overactivation across organ systems. Moreover, we summarise the evidence from preclinical studies and clinical trials that have set the stage for a potential new paradigm of MR antagonism.
Keywords: Eplerenone; Finerenone; Mineralocorticoid receptor; Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists; Review; Spironolactone.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Steroidal and Novel Non-steroidal Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists in Heart Failure and Cardiorenal Diseases: Comparison at Bench and Bedside.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2017;243:271-305. doi: 10.1007/164_2016_76. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27830348 Review.
-
Non-steroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists in cardiorenal disease.Eur Heart J. 2022 Aug 14;43(31):2931-2945. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehac299. Eur Heart J. 2022. PMID: 35713973
-
Effectiveness of nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists in patients with diabetic kidney disease.Postgrad Med. 2023 Apr;135(3):224-233. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2022.2060598. Epub 2022 Apr 20. Postgrad Med. 2023. PMID: 35392754 Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of finerenone for treatment of diabetic kidney disease: current knowledge and future perspective.Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2022 Sep;21(9):1161-1170. doi: 10.1080/14740338.2022.2130889. Epub 2022 Oct 6. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2022. PMID: 36174659 Review.
-
Finerenone : third-generation mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist for the treatment of heart failure and diabetic kidney disease.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2015;24(8):1123-35. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2015.1059819. Epub 2015 Jun 20. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2015. PMID: 26095025 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of L-type Ca2+-channels in the vasorelaxing response to finerenone in arteries of human visceral adipose tissue.Physiol Rep. 2024 Sep;12(18):e70062. doi: 10.14814/phy2.70062. Physiol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39317676 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Perspectives of Tubular Injury in Diabetic Kidney Disease: An Update.Biomedicines. 2025 Jun 10;13(6):1424. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13061424. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40564143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Effects: Steroidal and Nonsteroidal Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Jul 29;26(7):38690. doi: 10.31083/RCM38690. eCollection 2025 Jul. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40776944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intellectual landscapes and emerging trends of non-steroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists: a bibliometric and visual analysis.Int Urol Nephrol. 2024 Sep;56(9):3079-3090. doi: 10.1007/s11255-024-04059-9. Epub 2024 Apr 25. Int Urol Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38662266 Review.
-
Finerenone and semaglutide: Role in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.World J Cardiol. 2025 May 26;17(5):105822. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i5.105822. World J Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 40496391 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

