Case Study of Autopsy Findings in a Population of Post-COVID-19 Vaccination in Thailand
- PMID: 38127652
- PMCID: PMC11446518
- DOI: 10.1097/PAF.0000000000000900
Case Study of Autopsy Findings in a Population of Post-COVID-19 Vaccination in Thailand
Abstract
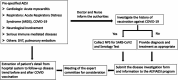
Thailand began offering the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccine nationwide in February 2021, with 1,885 deaths reported by the end of the year. Therefore, it is essential to assess the correlation between vaccination and cause of death from autopsy. This study included 34 autopsies of a deceased within 30 days after COVID-19 vaccination performed in Bangkok under the postmortem inquest service area of Bhumibol Adulyadej Hospital. The autopsies were performed by forensic pathologists. Moreover, detailed information about the deceased was collected, including age, sex, medical records, vaccination history, scene investigation reports, autopsy reports, cause of death, and a probable causal relationship between vaccination and cause of death. There were 24 males (70.59%), and the average age of the deceased was 52.76 years. Of all individuals, 28 (82.36%), 4 (11.76%), and 2 (5.88%) were vaccinated with AstraZeneca, Sinopharm, and SinoVac, respectively. The most common cause of death was ischemic heart disease (n = 17). None of the deceased patients had a causal relationship to the vaccine. Deaths were due to natural causes, as no definitive link between vaccination and cause of death was established in the study.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The author has no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Riffe T Acosta E, team tC-D . Data resource profile: COVerAGE-DB: a global demographic database of COVID-19 cases and deaths. International Journal of Epidemiology. 2021;50:390–390 f.
-
- Wise J. Covid-19: global death toll may three times higher than official records, study suggests. BMJ. 2022;376:o636. - PubMed
-
- Clemente-Suárez VJ Navarro-Jiménez E Moreno-Luna L, et al. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on social, health, and economy. Sustainability. 2021;13:6314.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical