Thiophene derivative inflicts cytotoxicity via an intrinsic apoptotic pathway on human acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells
- PMID: 38127921
- PMCID: PMC10734950
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0295441
Thiophene derivative inflicts cytotoxicity via an intrinsic apoptotic pathway on human acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells
Abstract
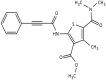
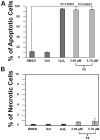
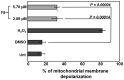
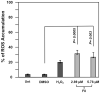
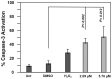
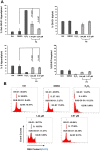
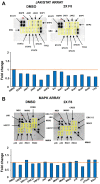
In an effort to identify novel anti-cancer agents, we employed a well-established High Throughput Screening (HTS) assay to assess the cytotoxic effect of compounds within the ChemBridge DIVERSet Library on a lymphoma cell line. This screen revealed a novel thiophene, F8 (methyl 5-[(dimethylamino)carbonyl]-4-methyl-2-[(3-phenyl-2-propynoyl) amino]-3-thiophenecarboxylate), that displays anti-cancer activity on lymphoma, leukemia, and other cancer cell lines. Thiophenes and thiophene derivatives have emerged as an important class of heterocyclic compounds that have displayed favorable drug characteristics. They have been previously reported to exhibit a broad spectrum of properties and varied uses in the field of medicine. In addition, they have proven to be effective drugs in various disease scenarios. They contain anti-inflammatory, anti-anxiety, anti-psychotic, anti-microbial, anti-fungal, estrogen receptor modulating, anti-mitotic, kinase inhibiting and anti-cancer activities, rendering compounds with a thiophene a subject of significant interest in the scientific community. Compound F8 consistently induced cell death at a low micromolar range on a small panel of cancer cell lines after a 48 h period. Further investigation revealed that F8 induced phosphatidylserine externalization, reactive oxygen species generation, mitochondrial depolarization, kinase inhibition, and induces apoptosis. These findings demonstrate that F8 has promising anti-cancer activity.
Copyright: © 2023 Swain et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel Tetrahydrobenzo [b] Thiophene Compounds Exhibit Anticancer Activity through Enhancing Apoptosis and Inhibiting Tyrosine Kinase.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2018;18(12):1761-1769. doi: 10.2174/1871520618666180813120558. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 30101717
-
Thiophene-2-carboxamide derivatives of anthraquinone: A new potent antitumor chemotype.Eur J Med Chem. 2021 Oct 5;221:113521. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113521. Epub 2021 May 24. Eur J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34082225
-
Amides of pyrrole- and thiophene-fused anthraquinone derivatives: A role of the heterocyclic core in antitumor properties.Eur J Med Chem. 2020 Aug 1;199:112294. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112294. Epub 2020 May 6. Eur J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32428792
-
5-Nitro-Thiophene-Thiosemicarbazone Derivatives Present Antitumor Activity Mediated by Apoptosis and DNA Intercalation.Curr Top Med Chem. 2019;19(13):1075-1091. doi: 10.2174/1568026619666190621120304. Curr Top Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31223089
-
A Review on Anticancer Activities of Thiophene and Its Analogs.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2020;20(19):1944-1965. doi: 10.2174/1389557520666200715104555. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32669077 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Compounds Featuring a Thiophene Carboxamide Scaffold: Synthesis, Characterization and Antiproliferative Evaluation.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 16;26(14):6823. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146823. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40725068 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

