Mammalian circadian clock proteins form dynamic interacting microbodies distinct from phase separation
- PMID: 38127982
- PMCID: PMC10756265
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2318274120
Mammalian circadian clock proteins form dynamic interacting microbodies distinct from phase separation
Abstract
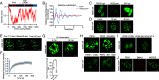
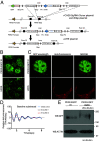
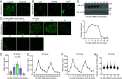
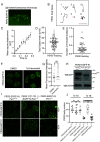
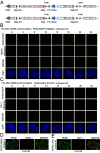
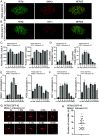
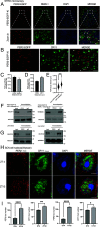
Liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) underlies diverse biological processes. Because most LLPS studies were performed in vitro using recombinant proteins or in cells that overexpress protein, the physiological relevance of LLPS for endogenous protein is often unclear. PERIOD, the intrinsically disordered domain-rich proteins, are central mammalian circadian clock components and interact with other clock proteins in the core circadian negative feedback loop. Different core clock proteins were previously shown to form large complexes. Circadian clock studies often rely on experiments that overexpress clock proteins. Here, we show that when Per2 transgene was stably expressed in cells, PER2 protein formed nuclear phosphorylation-dependent slow-moving LLPS condensates that recruited other clock proteins. Super-resolution microscopy of endogenous PER2, however, revealed formation of circadian-controlled, rapidly diffusing nuclear microbodies that were resistant to protein concentration changes, hexanediol treatment, and loss of phosphorylation, indicating that they are distinct from the LLPS condensates caused by protein overexpression. Surprisingly, only a small fraction of endogenous PER2 microbodies transiently interact with endogenous BMAL1 and CRY1, a conclusion that was confirmed in cells and in mice tissues, suggesting an enzyme-like mechanism in the circadian negative feedback process. Together, these results demonstrate that the dynamic interactions of core clock proteins are a key feature of mammalian circadian clock mechanism and the importance of examining endogenous proteins in LLPS and circadian clock studies.
Keywords: PERIOD protein; circadian clock; phase separation; protein interaction.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
Update of
-
Mammalian circadian clock proteins form dynamic interacting microbodies distinct from phase separation.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Oct 23:2023.10.19.563153. doi: 10.1101/2023.10.19.563153. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Dec 26;120(52):e2318274120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2318274120. PMID: 37961341 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Hastings M. H., Reddy A. B., Maywood E. S., A clockwork web: Circadian timing in brain and periphery, in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 4, 649–661 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Schmalen I., et al. , Interaction of circadian clock proteins CRY1 and PER2 is modulated by zinc binding and disulfide bond formation. Cell 157, 1203–1215 (2014). - PubMed

