Serine-129 phosphorylation of α-synuclein is an activity-dependent trigger for physiologic protein-protein interactions and synaptic function
- PMID: 38128479
- PMCID: PMC10766085
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2023.11.020
Serine-129 phosphorylation of α-synuclein is an activity-dependent trigger for physiologic protein-protein interactions and synaptic function
Abstract
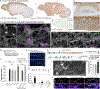
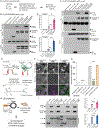
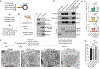
Phosphorylation of α-synuclein at the serine-129 site (α-syn Ser129P) is an established pathologic hallmark of synucleinopathies and a therapeutic target. In physiologic states, only a fraction of α-syn is phosphorylated at this site, and most studies have focused on the pathologic roles of this post-translational modification. We found that unlike wild-type (WT) α-syn, which is widely expressed throughout the brain, the overall pattern of α-syn Ser129P is restricted, suggesting intrinsic regulation. Surprisingly, preventing Ser129P blocked activity-dependent synaptic attenuation by α-syn-thought to reflect its normal function. Exploring mechanisms, we found that neuronal activity augments Ser129P, which is a trigger for protein-protein interactions that are necessary for mediating α-syn function at the synapse. AlphaFold2-driven modeling and membrane-binding simulations suggest a scenario where Ser129P induces conformational changes that facilitate interactions with binding partners. Our experiments offer a new conceptual platform for investigating the role of Ser129 in synucleinopathies, with implications for drug development.
Keywords: AlphaFold; CRISPR; alanine mutations; endogenous tagging; neuronal activity; pHluorin; proximity-ligation assay; serine phosphorylation; synapses; α-synuclein.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

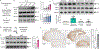



References
-
- Anderson JP, Walker DE, Goldstein JM, de Laat R, Banducci K, Caccavello RJ, Barbour R, Huang J, Kling K, Lee M, et al. (2006). Phosphorylation of Ser-129 is the dominant pathological modification of alpha-synuclein in familial and sporadic Lewy body disease. J Biol Chem 281, 29739–29752. M600933200 [pii]10.1074/jbc.M600933200. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fujiwara H, Hasegawa M, Dohmae N, Kawashima A, Masliah E, Goldberg MS, Shen J, Takio K, and Iwatsubo T (2002). alpha-Synuclein is phosphorylated in synucleinopathy lesions. Nat.Cell Biol 4, 160–164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

