Biallelic BORCS8 variants cause an infantile-onset neurodegenerative disorder with altered lysosome dynamics
- PMID: 38128568
- PMCID: PMC11068110
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awad427
Biallelic BORCS8 variants cause an infantile-onset neurodegenerative disorder with altered lysosome dynamics
Abstract
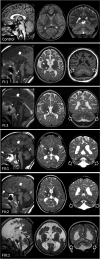
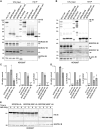
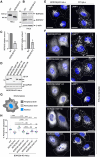
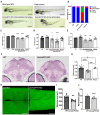
BLOC-one-related complex (BORC) is a multiprotein complex composed of eight subunits named BORCS1-8. BORC associates with the cytosolic face of lysosomes, where it sequentially recruits the small GTPase ARL8 and kinesin-1 and -3 microtubule motors to promote anterograde transport of lysosomes toward the peripheral cytoplasm in non-neuronal cells and the distal axon in neurons. The physiological and pathological importance of BORC in humans, however, remains to be determined. Here, we report the identification of compound heterozygous variants [missense c.85T>C (p.Ser29Pro) and frameshift c.71-75dupTGGCC (p.Asn26Trpfs*51)] and homozygous variants [missense c.196A>C (p.Thr66Pro) and c.124T>C (p.Ser42Pro)] in BORCS8 in five children with a severe early-infantile neurodegenerative disorder from three unrelated families. The children exhibit global developmental delay, severe-to-profound intellectual disability, hypotonia, limb spasticity, muscle wasting, dysmorphic facies, optic atrophy, leuko-axonopathy with hypomyelination, and neurodegenerative features with prevalent supratentorial involvement. Cellular studies using a heterologous transfection system show that the BORCS8 missense variants p.Ser29Pro, p.Ser42Pro and p.Thr66Pro are expressed at normal levels but exhibit reduced assembly with other BORC subunits and reduced ability to drive lysosome distribution toward the cell periphery. The BORCS8 frameshift variant p.Asn26Trpfs*51, on the other hand, is expressed at lower levels and is completely incapable of assembling with other BORC subunits and promoting lysosome distribution toward the cell periphery. Therefore, all the BORCS8 variants are partial or total loss-of-function alleles and are thus likely pathogenic. Knockout of the orthologous borcs8 in zebrafish causes decreased brain and eye size, neuromuscular anomalies and impaired locomotion, recapitulating some of the key traits of the human disease. These findings thus identify BORCS8 as a novel genetic locus for an early-infantile neurodegenerative disorder and highlight the critical importance of BORC and lysosome dynamics for the development and function of the central nervous system.
Keywords: hereditary spastic paraplegia; leukodystrophy; lysosomes; neurodegeneration; neurodevelopmental disorder.
Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
BLOC1S1 variants cause lysosomal and autophagic defects resulting in a hypomyelinating leukodystrophy with epileptic encephalopathy.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 17:2025.07.17.25331211. doi: 10.1101/2025.07.17.25331211. medRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40791729 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
BORC, a multisubunit complex that regulates lysosome positioning.Dev Cell. 2015 Apr 20;33(2):176-88. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2015.02.011. Dev Cell. 2015. PMID: 25898167 Free PMC article.
-
BORC Functions Upstream of Kinesins 1 and 3 to Coordinate Regional Movement of Lysosomes along Different Microtubule Tracks.Cell Rep. 2016 Nov 15;17(8):1950-1961. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.10.062. Cell Rep. 2016. PMID: 27851960 Free PMC article.
-
A novel pathogenic variant in the 3' end of the AGTPBP1 gene gives rise to neurodegeneration without cerebellar atrophy: an expansion of the disease phenotype?Neurogenetics. 2021 May;22(2):127-132. doi: 10.1007/s10048-021-00643-8. Epub 2021 Apr 28. Neurogenetics. 2021. PMID: 33909173 Review.
-
Arf-like GTPase Arl8: Moving from the periphery to the center of lysosomal biology.Cell Logist. 2015 Sep 21;5(3):e1086501. doi: 10.1080/21592799.2015.1086501. eCollection 2015 Jul-Sep. Cell Logist. 2015. PMID: 27057420 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
KIF9 Ameliorates Neuropathology and Cognitive Dysfunction by Promoting Macroautophagy in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease.Aging Cell. 2025 May;24(5):e14490. doi: 10.1111/acel.14490. Epub 2025 Jan 19. Aging Cell. 2025. PMID: 39829171 Free PMC article.
-
Disruptions in axonal lysosome transport and its contribution to neurological disease.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2024 Aug;89:102382. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2024.102382. Epub 2024 Jun 20. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38905918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maintenance of neuronal TDP-43 expression requires axonal lysosome transport.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 30:2024.09.30.615241. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.30.615241. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 39803527 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction, cause or consequence in neurodegenerative diseases?Bioessays. 2025 Jan;47(1):e2400023. doi: 10.1002/bies.202400023. Epub 2024 Oct 4. Bioessays. 2025. PMID: 39367555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenic variants in BORCS5 Cause a Spectrum of Neurodevelopmental and Neurodegenerative Disorders with Lysosomal Dysfunction.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 7:2025.04.30.25326597. doi: 10.1101/2025.04.30.25326597. medRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40385417 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Hofmann I, Munro S. An N-terminally acetylated Arf-like GTPase is localised to lysosomes and affects their motility. J Cell Sci. 2006;119:1494–1503. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

