UBE2O reduces the effectiveness of interferon-α via degradation of IFIT3 in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 38129382
- PMCID: PMC10740027
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-023-06369-9
UBE2O reduces the effectiveness of interferon-α via degradation of IFIT3 in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
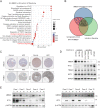
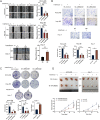
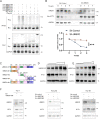
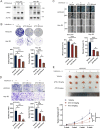
Interferon (IFN) exerts its effects through interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs), but its efficacy is limited by interferon resistance, which can be caused by the ubiquitination of key proteins. UBE2O was initially identified as a promising therapeutic target based on data from the TCGA and iUUCD 2.0 databases. Through the inhibition of UBE2O, interferon α/β signaling and overall interferon signaling were activated. Integrating data from proteomic, mass spectrometry, and survival analyses led to the identification of IFIT3, a mediator of interferon signaling, as a ubiquitination substrate of UBE2O. The results of in vitro and in vivo experiments demonstrated that the knockdown of UBE2O can enhance the efficacy of interferon-α by upregulating IFIT3 expression. K236 was identified as a ubiquitination site in IFIT3, and the results of rescue experiments confirmed that the effect of UBE2O on interferon-α sensitivity is dependent on IFIT3 activity. ATO treatment inhibited UBE2O and increased IFIT3 expression, thereby increasing the effectiveness of interferon-α. In conclusion, these findings suggest that UBE2O worsens the therapeutic effect of interferon-α by targeting IFIT3 for ubiquitination and degradation.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Kao KC, Jaccard A, Ho PC. IFNalpha potentiates immune-checkpoint blockade by rewiring metabolic cross-talk. Cancer Discov. 2022;12:1615–6. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-22-0472. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

