Identification, evolution, and expression of GDSL-type Esterase/Lipase (GELP) gene family in three cotton species: a bioinformatic analysis
- PMID: 38129780
- PMCID: PMC10734139
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-023-09717-3
Identification, evolution, and expression of GDSL-type Esterase/Lipase (GELP) gene family in three cotton species: a bioinformatic analysis
Abstract
Background: GDSL esterase/lipases (GELPs) play important roles in plant growth, development, and response to biotic and abiotic stresses. Presently, an extensive and in-depth analysis of GELP family genes in cotton is still not clear enough, which greatly limits the further understanding of cotton GELP function and regulatory mechanism.
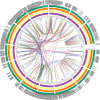
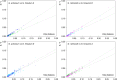
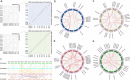
Results: A total of 389 GELP family genes were identified in three cotton species of Gossypium hirsutum (193), G. arboreum (97), and G. raimondii (99). These GELPs could be classified into three groups and eight subgroups, with the GELPs in same group to have similar gene structures and conserved motifs. Evolutionary event analysis showed that the GELP family genes tend to be diversified at the spatial dimension and certain conservative at the time dimension, with a trend of potential continuous expansion in the future. The orthologous or paralogous GELPs among different genomes/subgenomes indicated the inheritance from genome-wide duplication during polyploidization, and the paralogous GELPs were derived from chromosomal segment duplication or tandem replication. GELP genes in the A/D subgenome underwent at least three large-scale replication events in the evolutionary process during the period of 0.6-3.2 MYA, with two large-scale evolutionary events between 0.6-1.8 MYA that were associated with tetraploidization, and the large-scale duplication between 2.6-9.1 MYA that occurred during diploidization. The cotton GELPs indicated diverse expression patterns in tissue development, ovule and fiber growth, and in response to biotic and abiotic stresses, combining the existing cis-elements in the promoter regions, suggesting the GELPs involvements of functions to be diversification and of the mechanisms to be a hormone-mediated manner.
Conclusions: Our results provide a systematic and comprehensive understanding the function and regulatory mechanism of cotton GELP family, and offer an effective reference for in-depth genetic improvement utilization of cotton GELPs.
Keywords: Biotic and abiotic stress; Cotton GDSL esterase/lipase; Evolution; Fiber growth; Tissue development; Transcriptomic expression; Whole genome duplication.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

